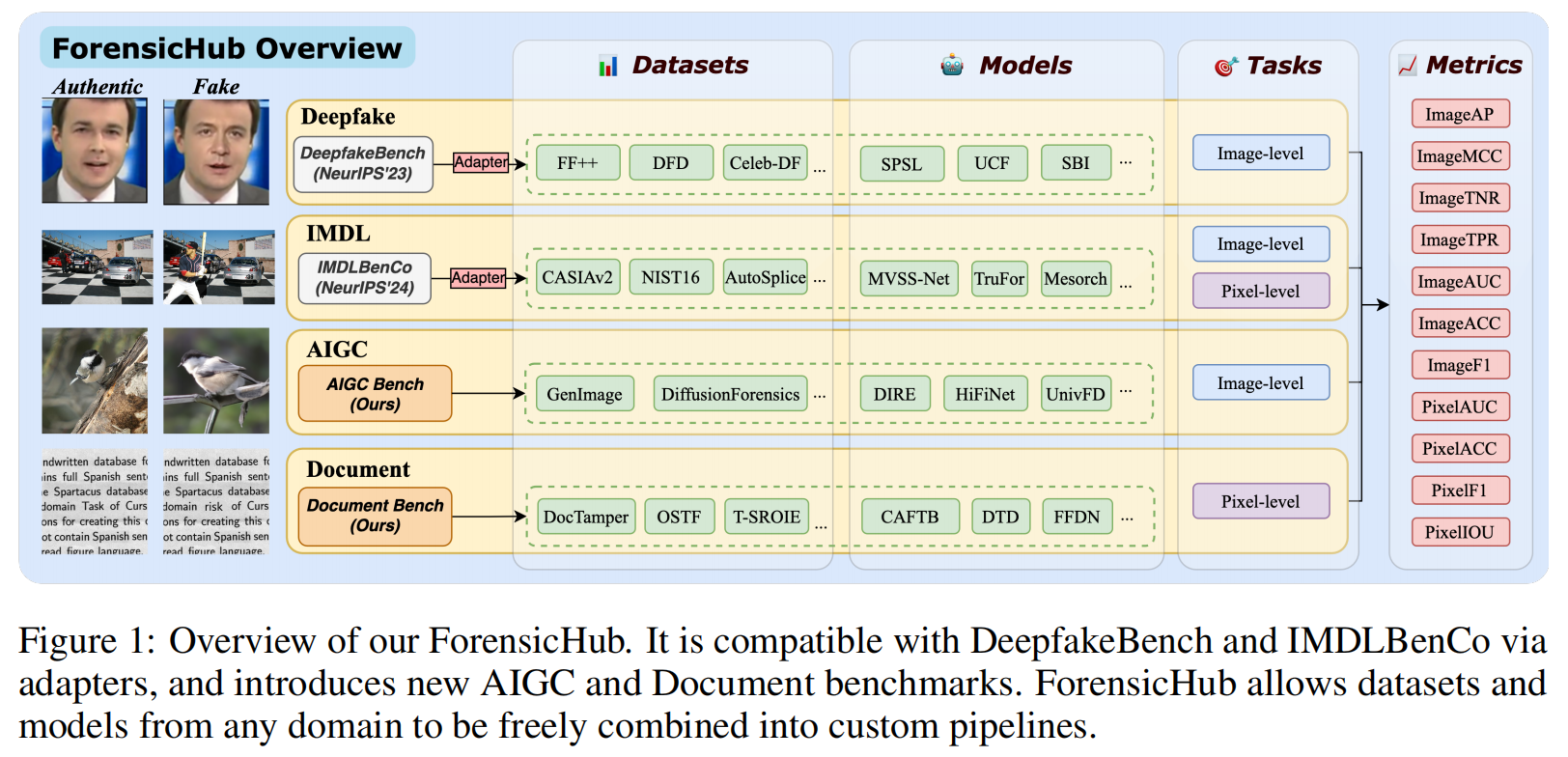
发表于arxiv上的论文,非常棒的工作!其整合了深度伪造检测、图像篡改检测/定位、AI生成图像检测和文档图像处理定位四大任务,并基于基准实验,提出了独特的发现。
2025年7月17日

发表于CVPR2024,。
2025年12月25日
发表于ACM MM 2022,基于不确定性感知原型transformer,该模型同时考虑异常区域的多样性和不确定性,从而实现精准的像素级视觉异常检测。
2025年12月18日
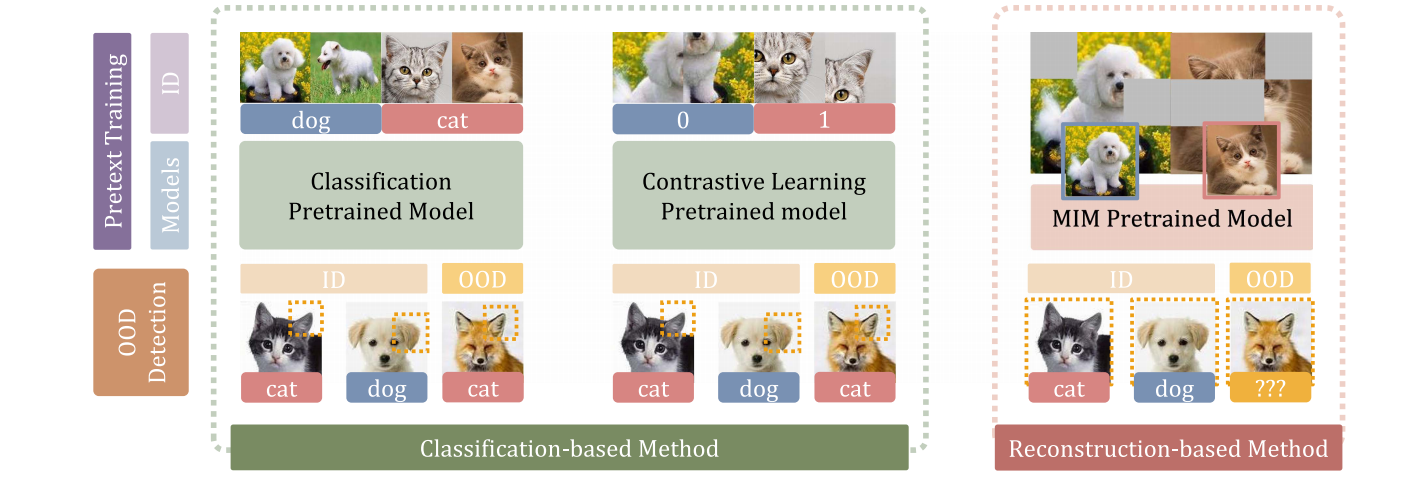
发表于TIFS 2024,采用基于重构的方法实现 OOD 检测,发现无需微调,基于重构的预训练模型在OOD检测任务上表现优秀。
2025年11月12日
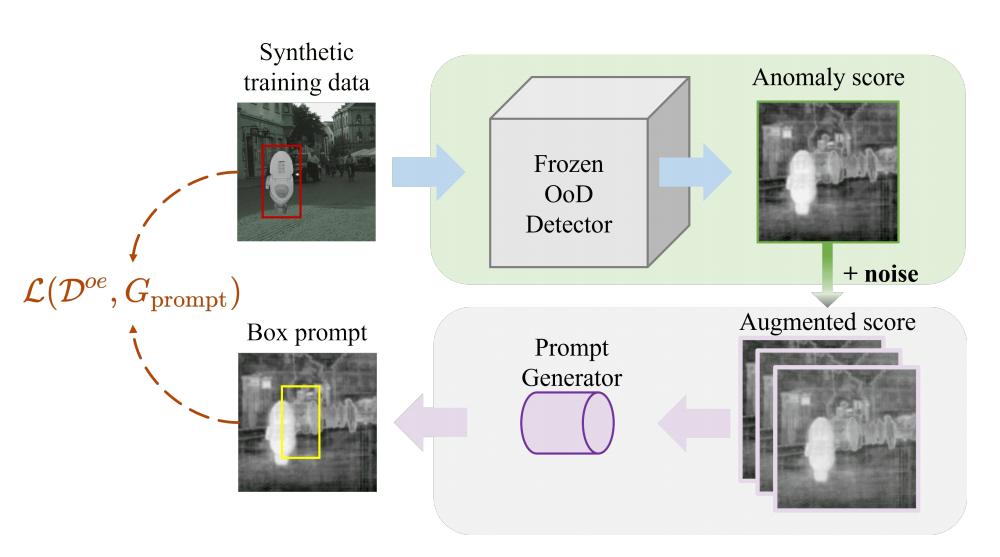
发表于CVPR 2024,探索了OOD检测的分割算法,本质上是将SAM模型加入到了OOD检测的分割任务,将传统OOD检测得到的异常分数图变成预测提示框,指导mask解码器定位OOD区域。
2025年11月12日
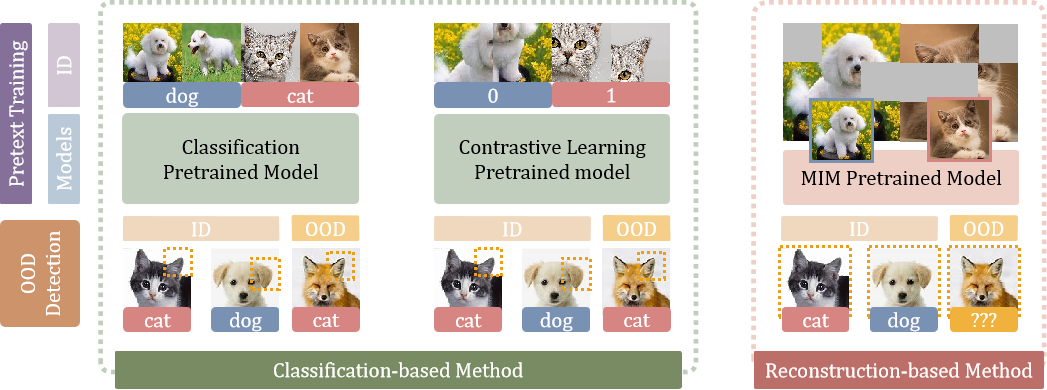
发表于CVPR 2023,采用基于重构的方法实现 OOD 检测,认为掩码图像建模任务可以顺利学习到图像自身的分布,实验结果达到了sota。
2025年11月11日
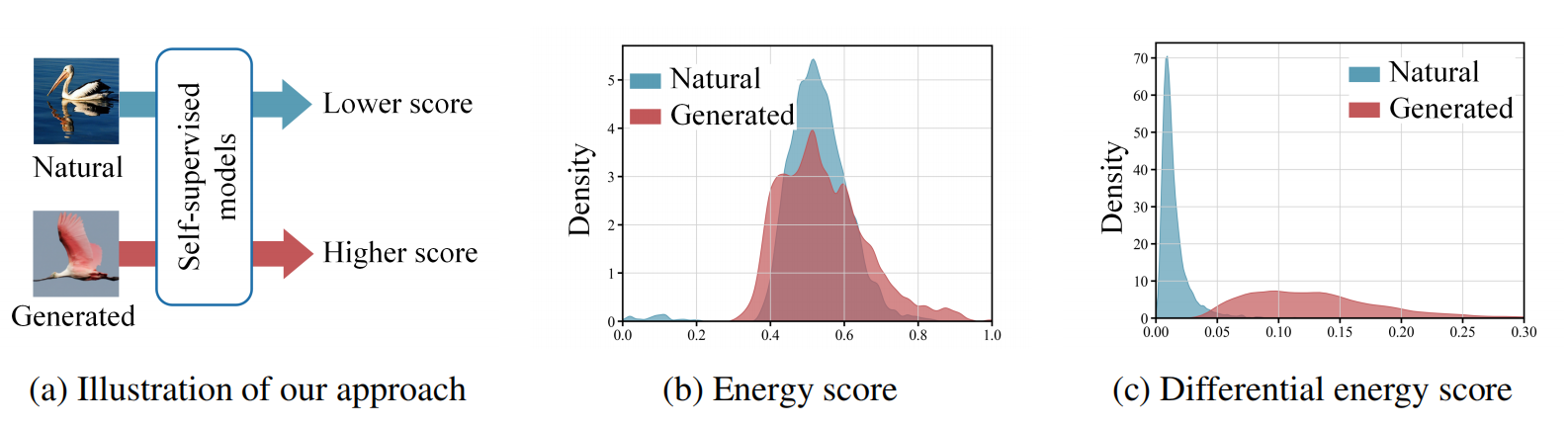
发表于NeurIPS 2025,完全基于自然图像训练的模型在生成图像检测,提出无需生成图片训练的方法DEnD,天才般的想法,与博主之前的某个想法不谋而合,无需训练便能达到sota,厉害!
2025年11月10日
发表于ICCV 2025。
2025年11月10日
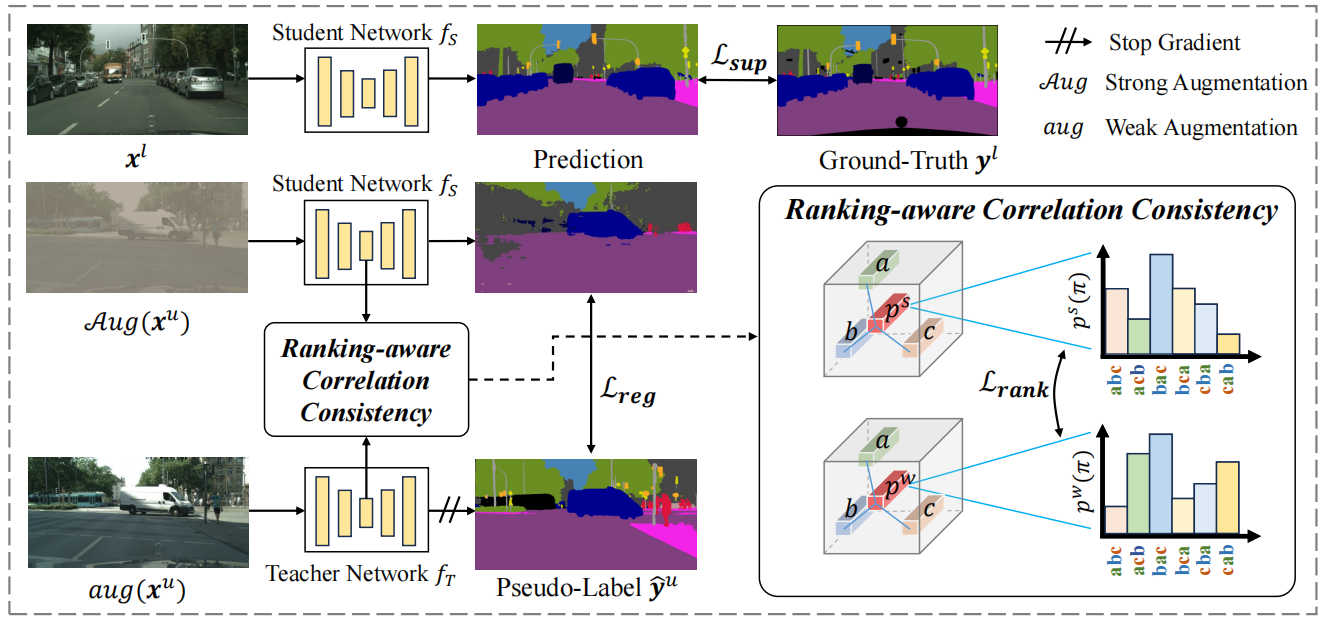
发表于CVPR2024,其为每个像素设置代理模型以超越常规像素级一致性,还通过建模代理间关系实现等级感知的关联一致性,从而充分释放代理潜力。
2025年11月4日
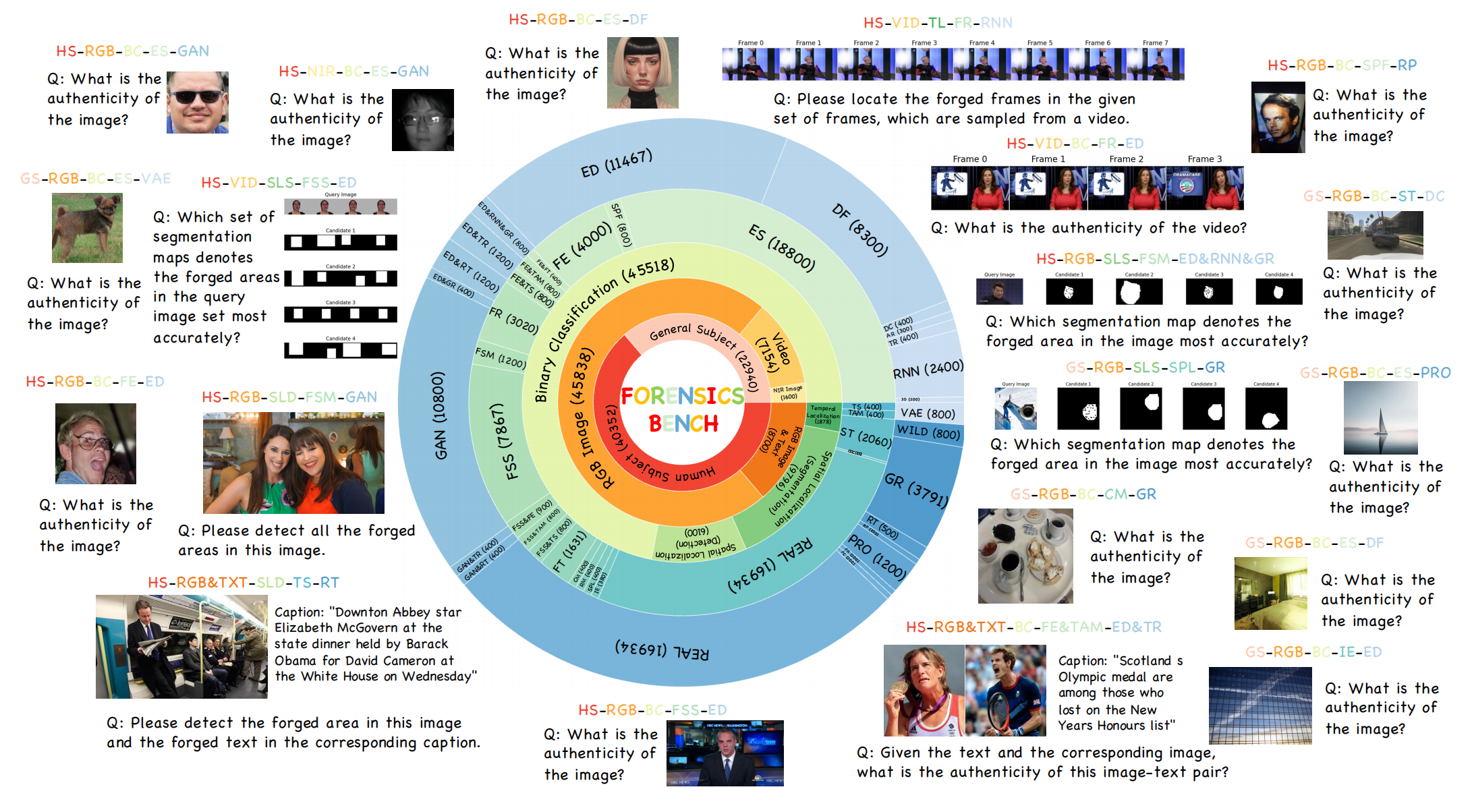
发表于CVPR2025,提出了Forensics-Bench,统一了所有基于大型视觉语言模型LVLMs的伪造检测器,并基于基准实验,提出了独特的发现。
2025年9月15日
发表于CVPR2022。
2025年9月12日
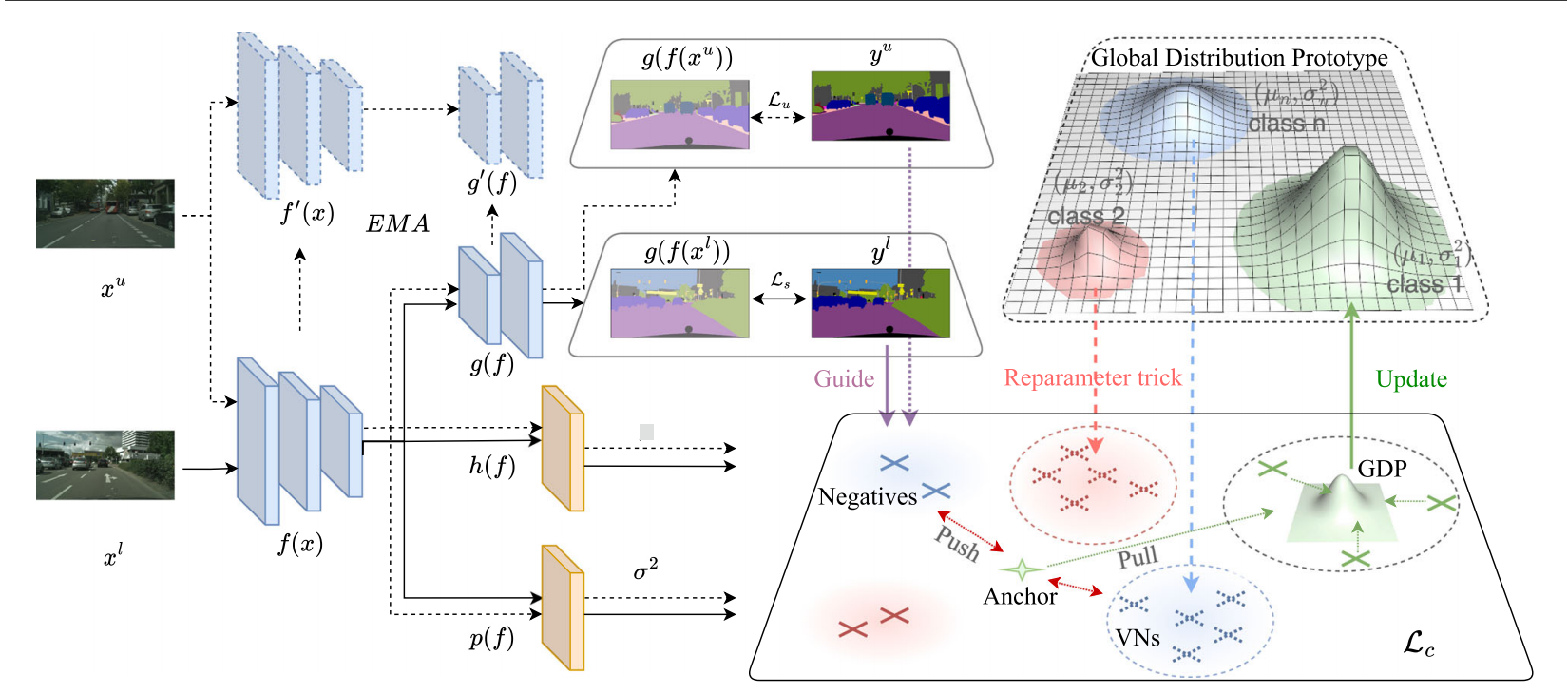
发表于IJCV2024,同时是AAAI 2023的oral,将对比学习引入到师生网络,本文提出使用多元高斯分布将像素级表示建模为概率表示(PR)。PR包含一个捕获最可能表示的均值向量和一个表示可靠性的方差向量。PR之间的相似性是通过相互似然评分来衡量的,该评分减少了不确定表示的影响。对于第二个问题,引入了全球分布原型(GDP),以在整个训练过程中聚合全球表示,确保原型位置的一致性。此外,虚拟负片可以从GDP中有效地生成,以补偿零碎的负分布,而不需要内存库。。
2025年9月4日
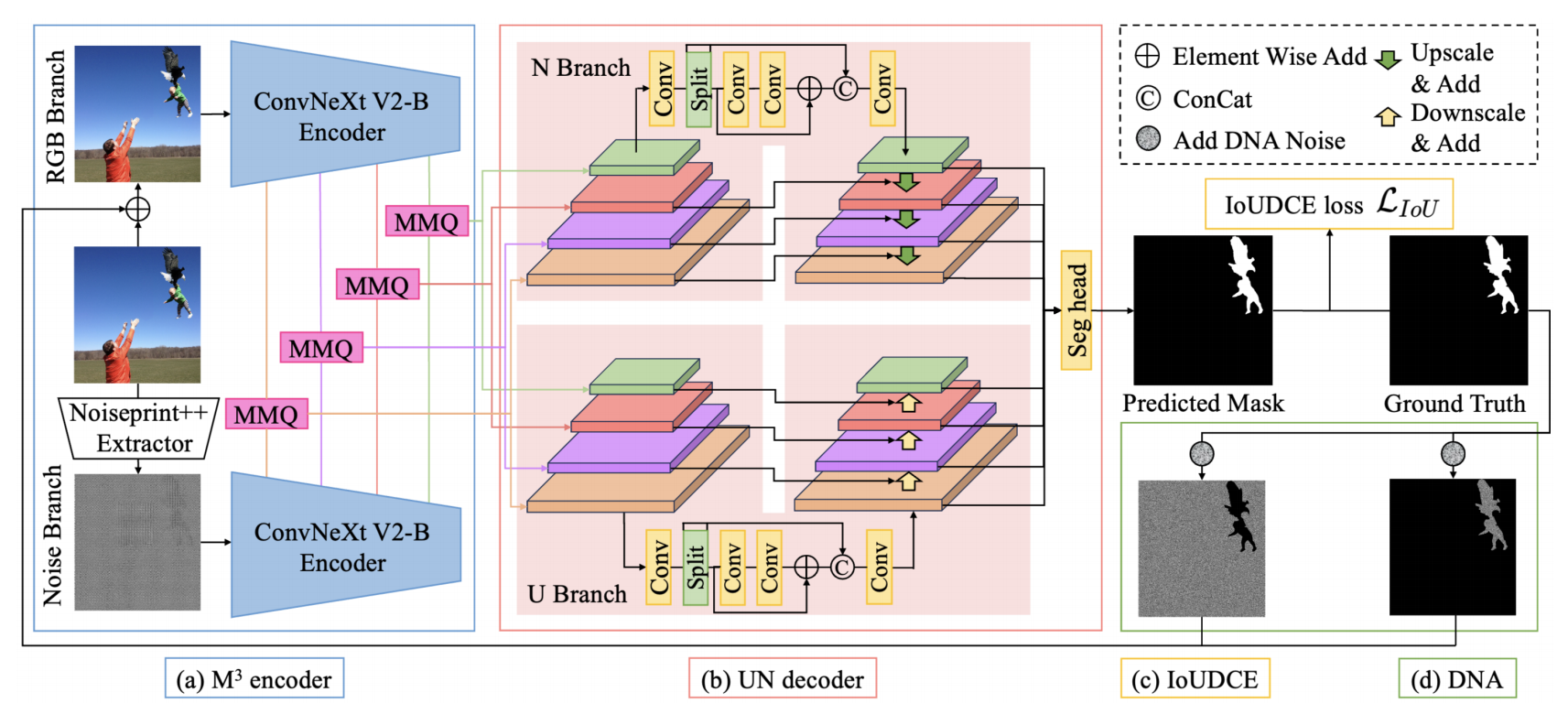
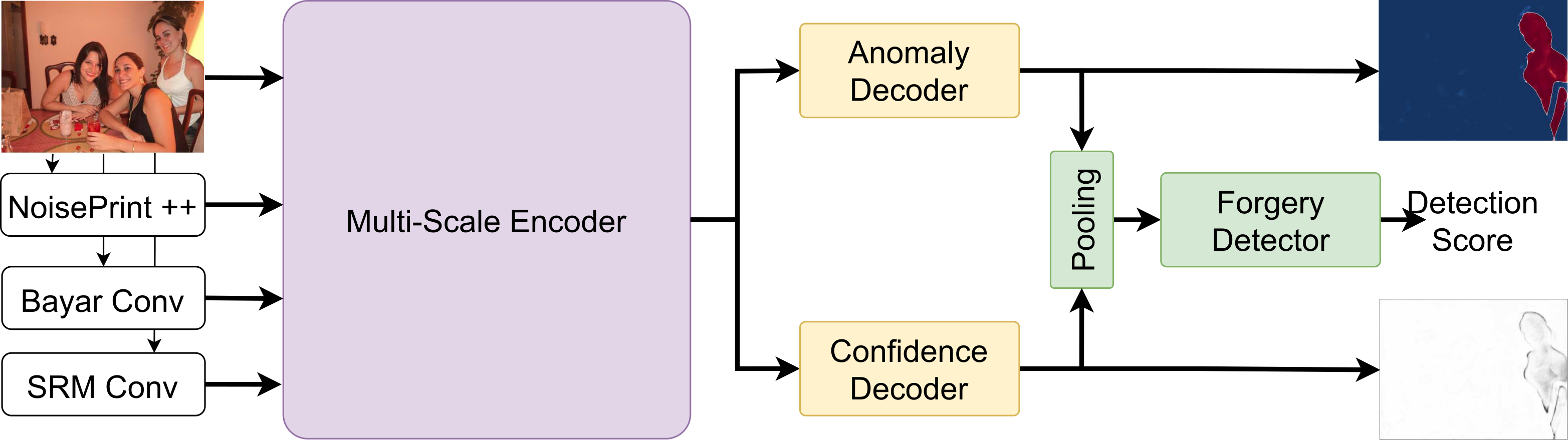
发表于AAAI 2025,其使用了Noiseprint++作为低级特征提取器,使用双流结构,其使用池化操作之后的结构作为查询向量,进行融合是最大的创新点。
2025年8月21日
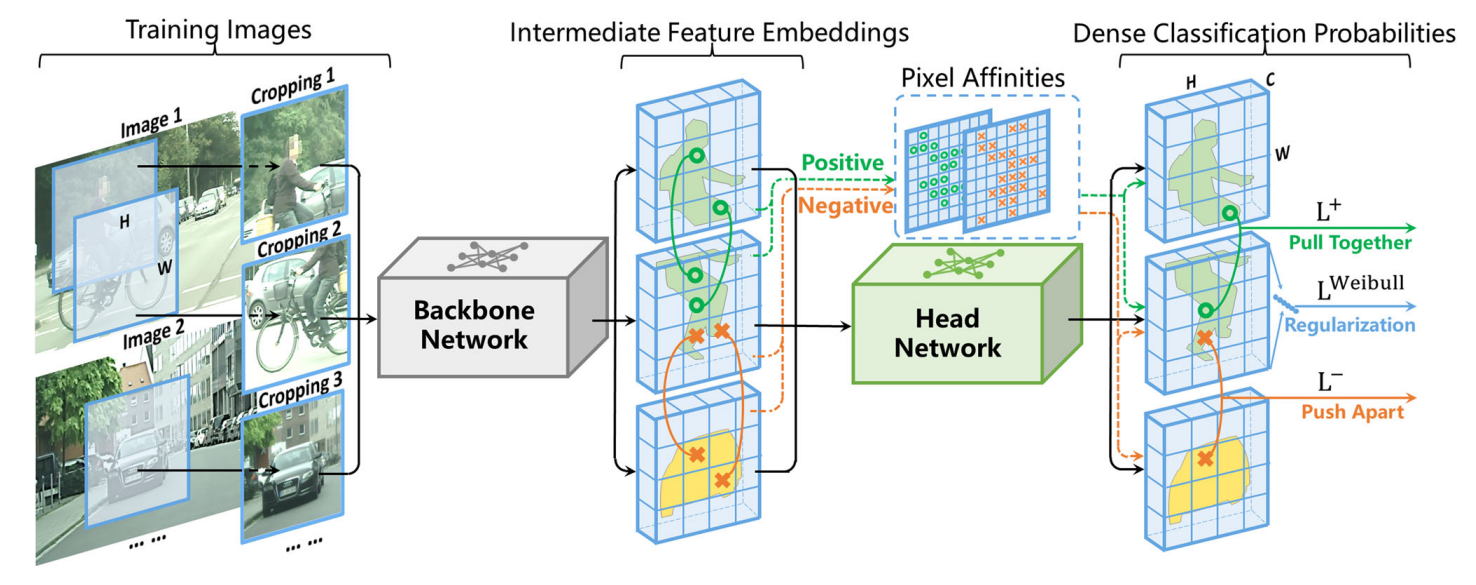
发表于IJCV 2024,其设计了一张基于类别不平衡判别式聚类的端到端的无监督语义分割的方法,其主要架构是backbone+分割头组成,其中分割头由两个ReLU激活的卷积层和一个Softmax激活的卷积层组成,最大的创新在于基于任务设计的损失函数。
2025年8月15日
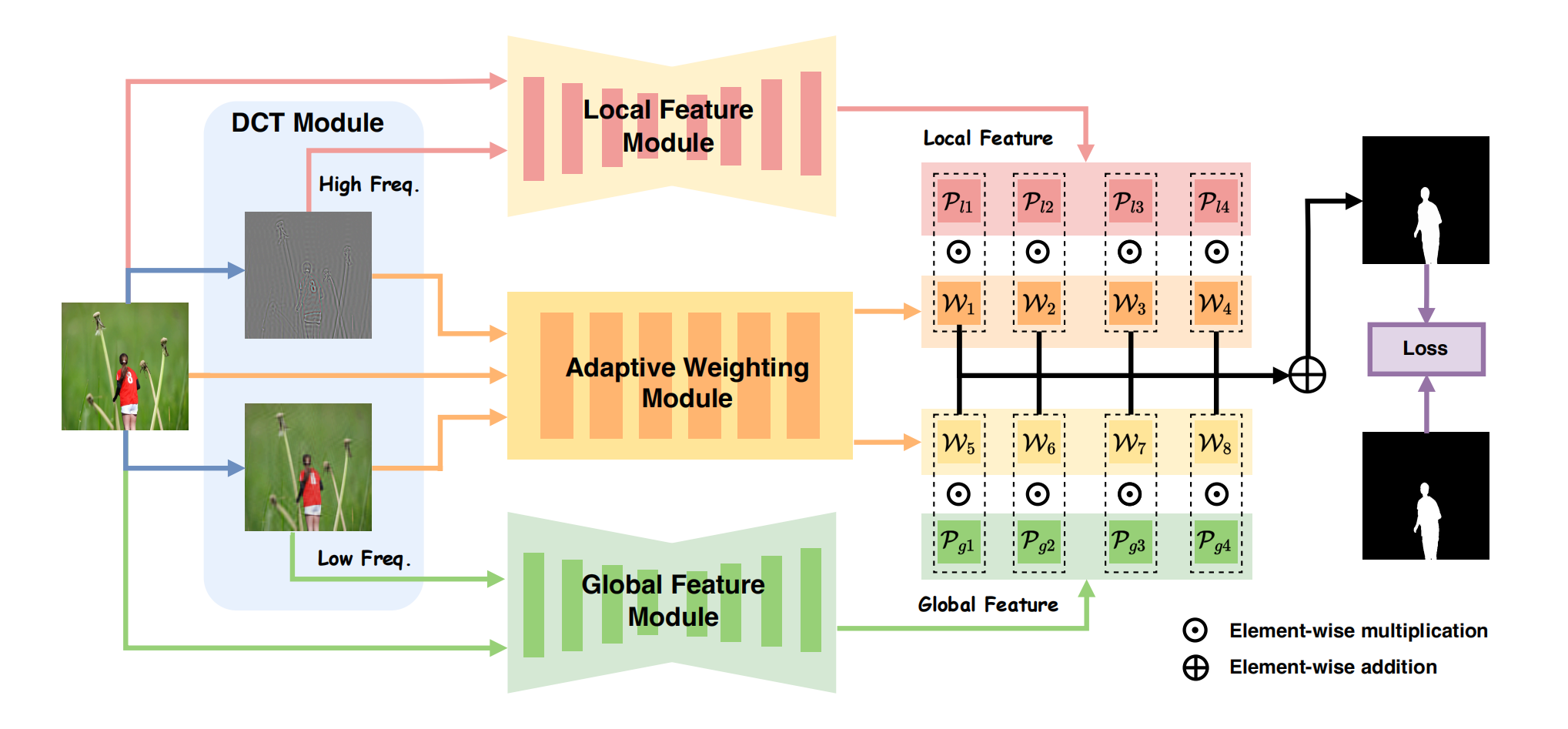
发表于AAAI2025,该论文Mesorch同时构建IML所需的微观与宏观信息介观表征,并提出Mesorch架构,一种融合卷积神经网络和Transformer模型优势的混合模型,通过动态调整尺度权重,能高效捕捉介观层面的伪影特征。
2025年8月6日
发表于TIFS 2025,,通过在特征提取网络阶段使用dropout层让同样的图像可以得到不同的输出特征,基于此,使用了两阶段训练,第一阶段在图像内部、跨尺度和跨模态三个维度使用对比损失进行训练,第二阶段使用交叉熵训练定位头,其代码思路和FOCAL非常相似。
2025年8月1日
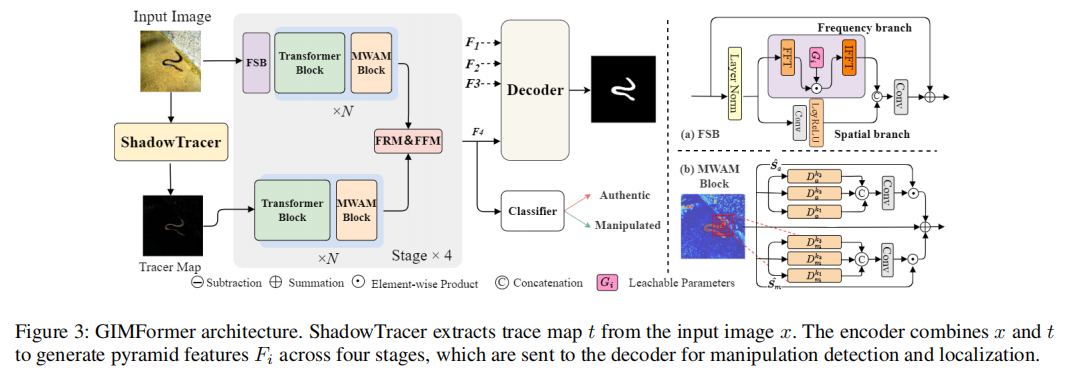
发表于AAAI2025,提出了GIM数据集,提出了双流网络GIMFormer。
2025年8月1日
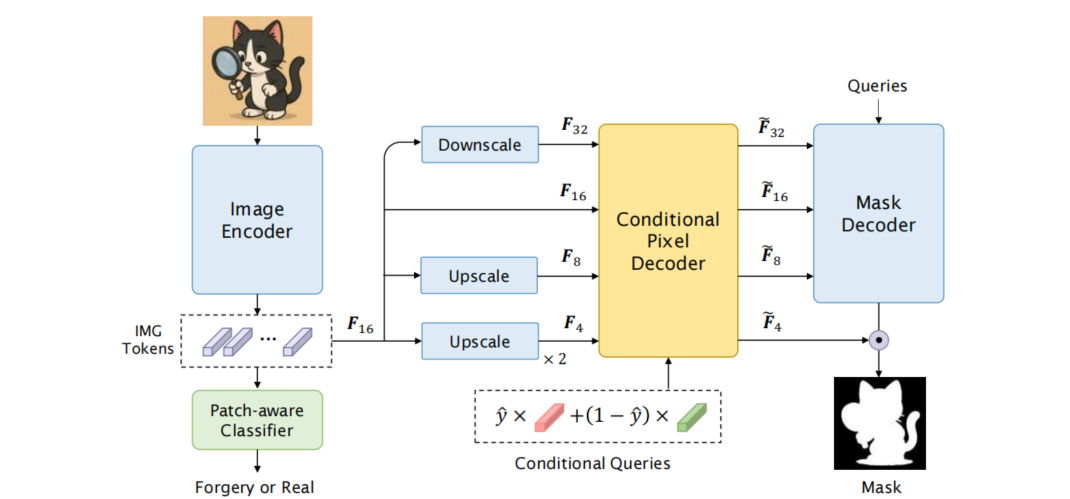
发表于IJCAI 2025,Loupe通过整合补丁感知分类器与带条件查询的分割模块,实现了全局真实性分类与细粒度掩码预测的同步处理。为增强对测试集分布偏移的鲁棒性,该模型创新性地采用伪标签引导的测试时自适应机制,利用补丁级预测结果对分割头进行监督学习。。
2025年7月26日
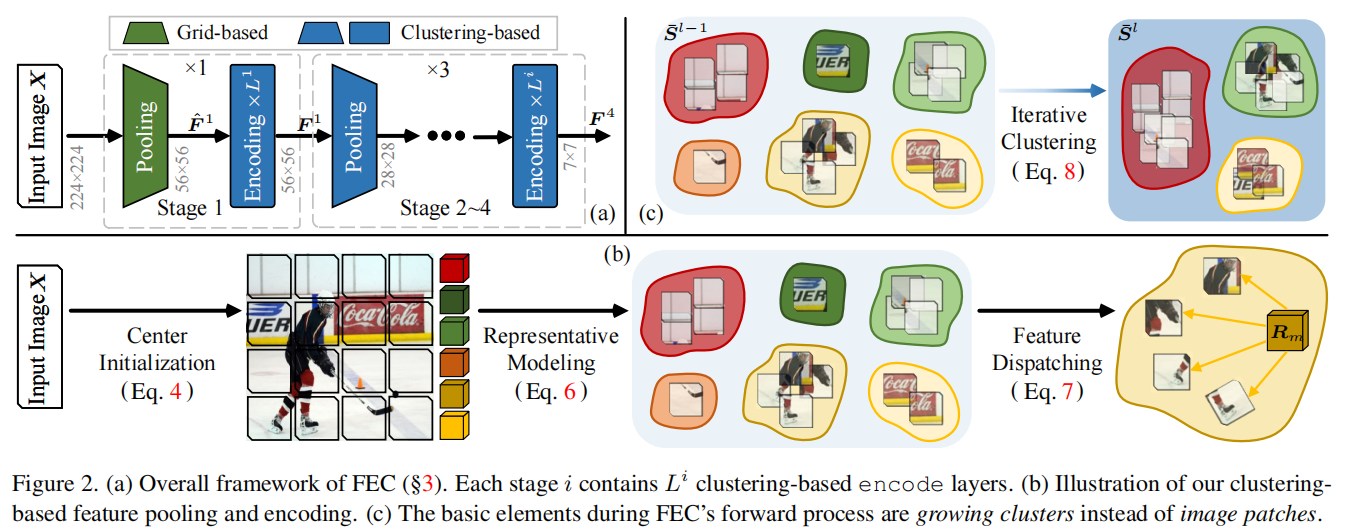
发表于CVPR2024,认为现有图像视觉提取器基于图片是平滑的这一假设设计了基于网格式的架构,因此提出了聚类特征提取FEC,在图像处理中,FEC算法通过两种交替操作实现:首先将像素分组为独立簇以提取抽象特征,随后利用当前特征向量更新像素的深度特征。这种迭代机制通过多层神经网络实现,最终生成的特征向量可直接应用于下游任务。各层间的聚类分配过程可供人工观察验证,使得FEC的前向计算过程完全透明化,并赋予其出色的自适应可解释性。
2025年7月22日
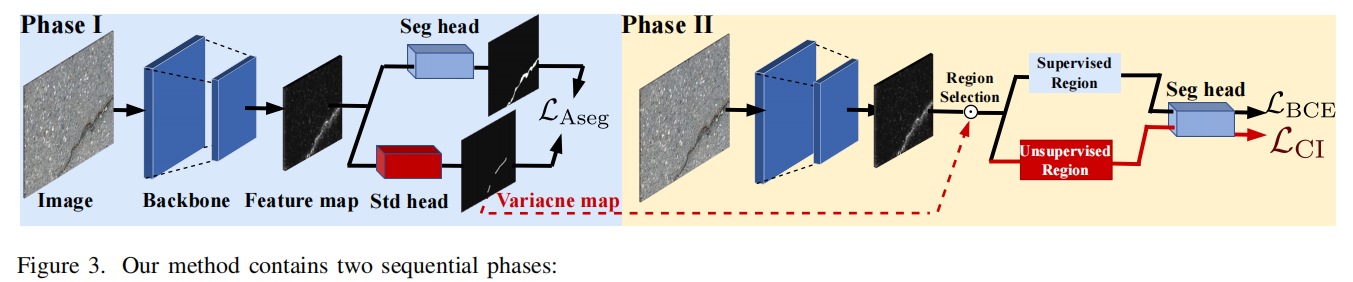
发表于CVPR2024,提出了一种基于聚类启发的表征学习框架,该框架包含自动裂缝分割的双阶段策略。第一阶段通过预处理步骤实现边缘非裂缝区域的精确定位。在第二阶段,为学习这些区域的判别性特征,我们设计了聚类启发式损失(CI Loss,*clustering-inspired loss*),将监督学习模式转变为无监督聚类方式。
2025年7月21日
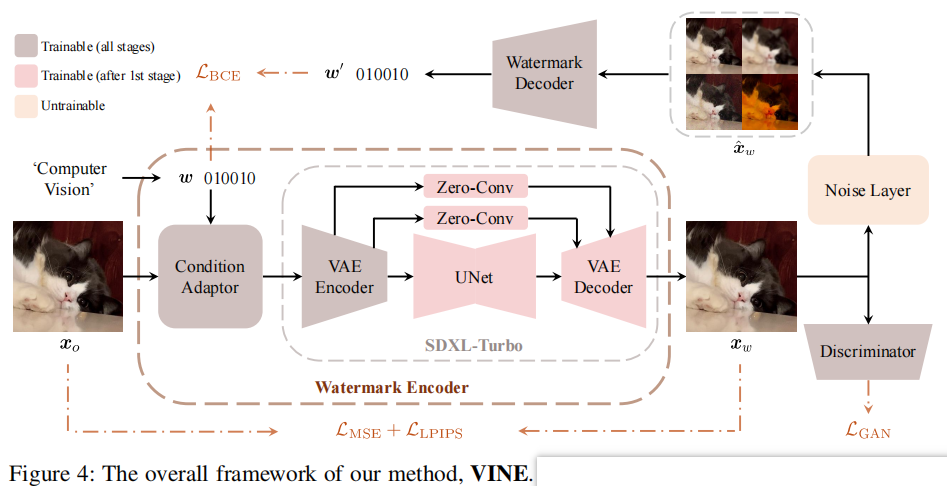
发表于ICLR2025,在本工作中,介绍了W-Bench,这是第一个全面的基准,旨在评估水印方法对广泛的图像编辑技术的鲁棒性,包括图像再生、全局编辑、局部编辑和图像到视频生成。通过实验发现图像编辑一般会消除中高频的信息,所以需要将水印信息保存在低频中
2025年7月18日
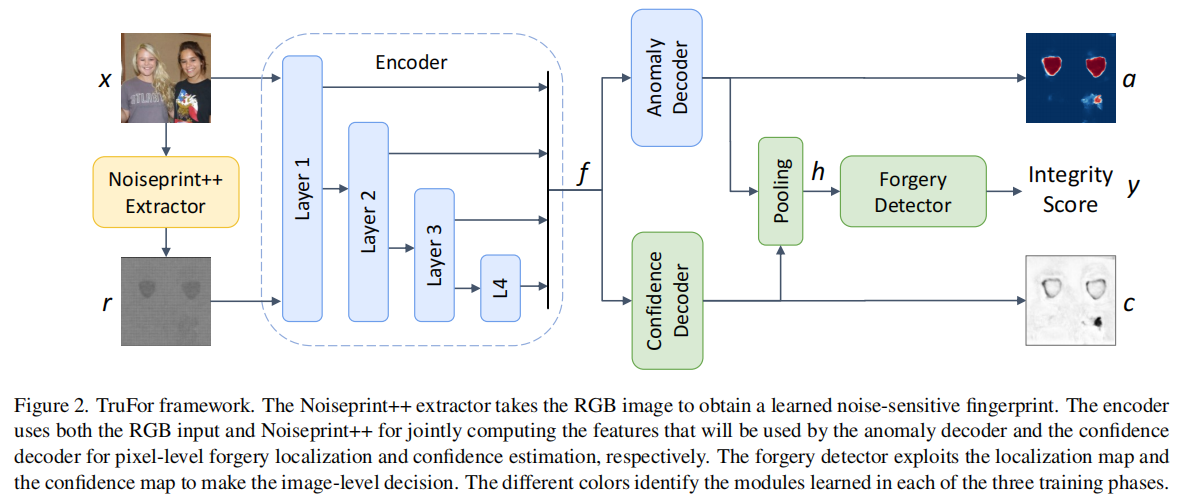
发表于CVPR2023,该框架通过基于Transformer的融合架构,同时提取高阶特征与低阶特征:前者整合RGB图像与自适应学习的噪声敏感指纹,后者则通过仅使用真实数据进行自监督训练,精准捕捉相机内外部处理产生的伪影特征。
2025年7月15日
发表于TPAMI2025,将输入图像分割成多个区块后,分别使用掩码自注意力和差异卷积分别建模全局和局部像素依赖,同时设计了新型的学习加权模块来融合全局和局部的特征,还设计了像素不一致性数据增强方法增强鲁棒性。但其比较论文实验的结果和原本论文在相同数据集相同指标下的结果相差太多,之后尝试在已给代码上进行测试,再完成之后阅读。
2025年7月15日
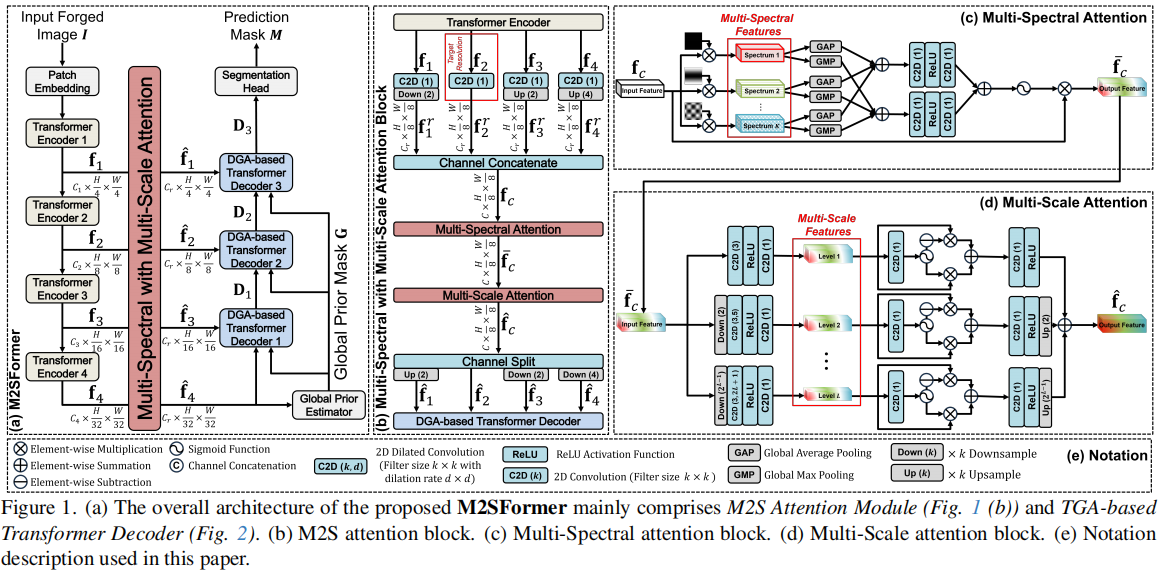
发表于ICCV2025,拿到了Highlight,M2SFormer通过在跳跃连接中统一多频段和多尺度注意力机制,借助全局上下文信息,能更精准捕捉各类伪造特征。此外,框架通过采用全局先验图(一种反映伪造检测难度的曲率度量指标)来解决上采样过程中细节丢失的问题。该方法使用分割的指标而不是图像篡改的传统指标,而且比较的方法并不是公认的sota。
2025年7月15日
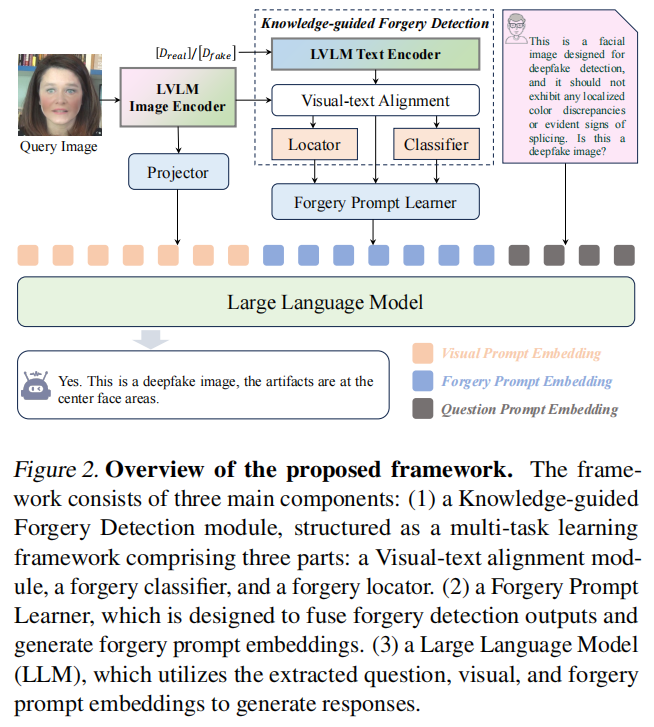
发表于ICML2025,将细粒度的伪造特征转化为语言模型的输入,在LLM提示调优后,得到解释性的deepfake检测结果。
2025年7月7日
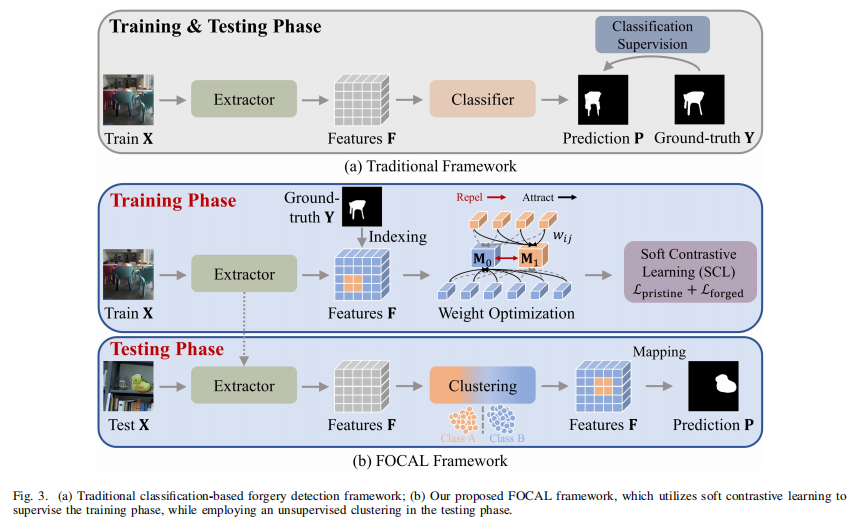
TDSC2025的文章,首次使用对比学习加聚类的方法做图像篡改检测。
2025年7月3日
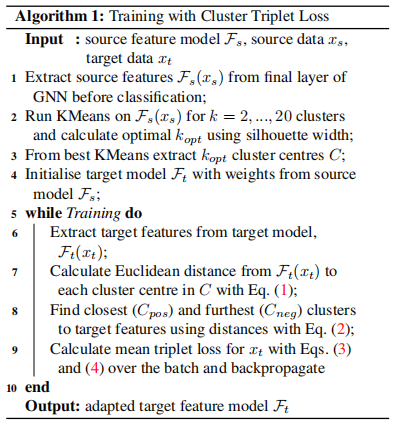
发表于CVPR2024,提出了一种新的无监督域适应方法,该方法采用聚类三元组损失函数,仅使用源域中的少量信息,从而提升目标域的性能。以源域中的重要节点的聚类中心为锚点,通过三元组损失,将目标域锚定到这些固定的聚类中心。源域的完美结构应该与目标域的完美结构相似,才能用作锚点。
2025年7月2日
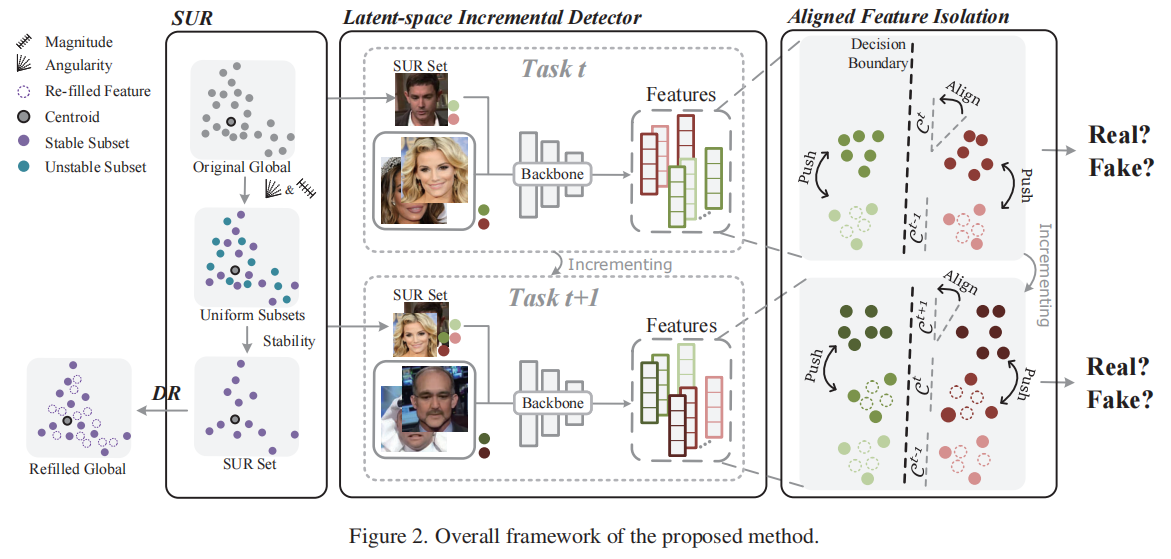
发表于CVPR2025,一个未经充分训练的IFFD模型在处理新的伪造时容易出现灾难性遗忘,这是因为将所有伪造都视为单一的“假”类别,导致不同类型的伪造品相互覆盖,从而导致早期任务中独特特征的遗忘,这存在于所有的IDF任务中,该论文提出了一种方法,通过将先前任务和新任务的潜在特征分布逐块堆叠,实现特征的对齐隔离。为了保留已学习到的伪造信息,并通过最小化分布重叠来积累新知识,从而减轻灾难性遗忘。首先引入了稀疏均匀回放(SUR),以获取可以视为先前全局分布的均匀稀疏版本的代表性子集。接着,我们提出了一个潜在空间增量检测器(LID),该检测器利用SUR数据来隔离和对齐分布。
2025年7月2日
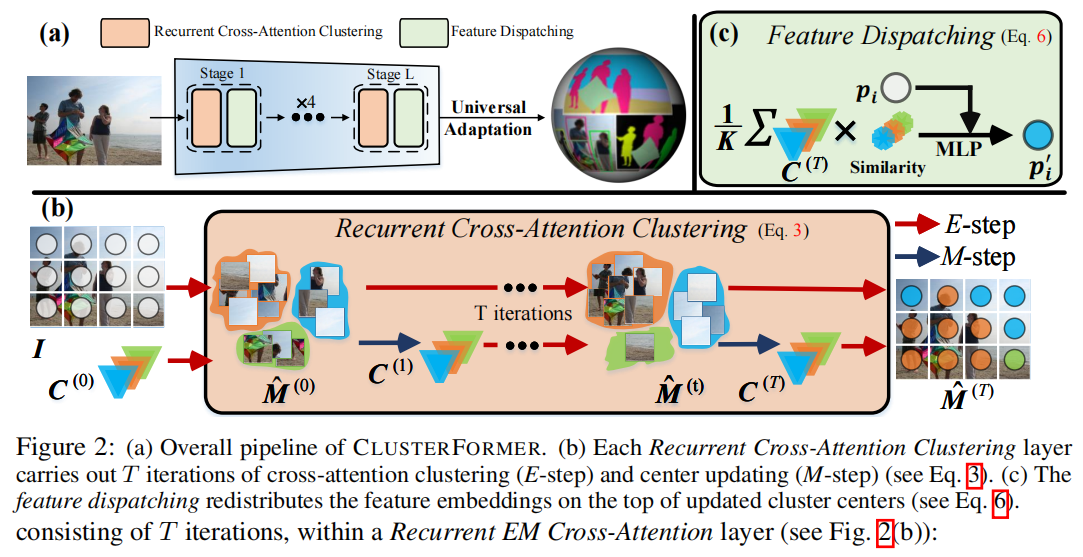
发表于NeurIPS2023,本文介绍了一种基于CLUSTERing范式与TransFORMER的通用视觉模型——CLUSTERFORMER。该模型包含两个创新设计:①循环交叉注意力聚类,重新定义了TransFORMER中的交叉注意力机制,通过递归更新聚类中心,促进强大的表示学习;②特征调度,利用更新后的聚类中心,通过基于相似性的度量重新分配图像特征,形成一个透明的处理流程。
2025年7月1日
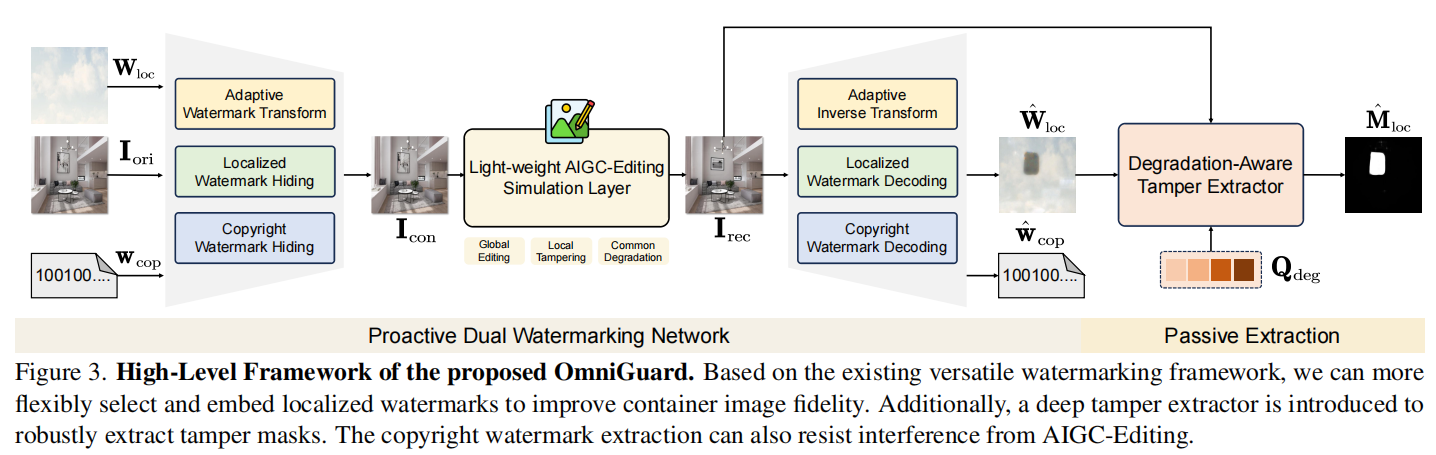
发表于CVPR2025,将版权水印和图像篡改主动保护两个任务联合起来。
2025年7月1日
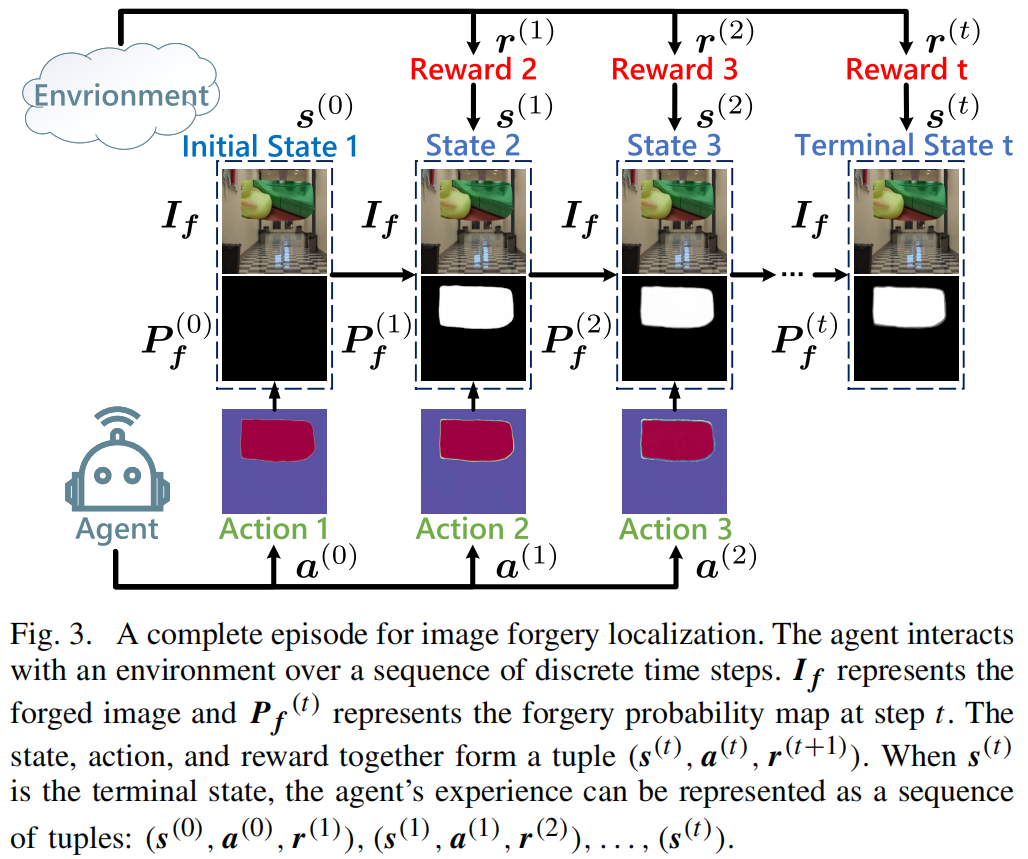
发表于TIFS2024,将强化学习引入到了图像篡改检测。
2025年5月19日
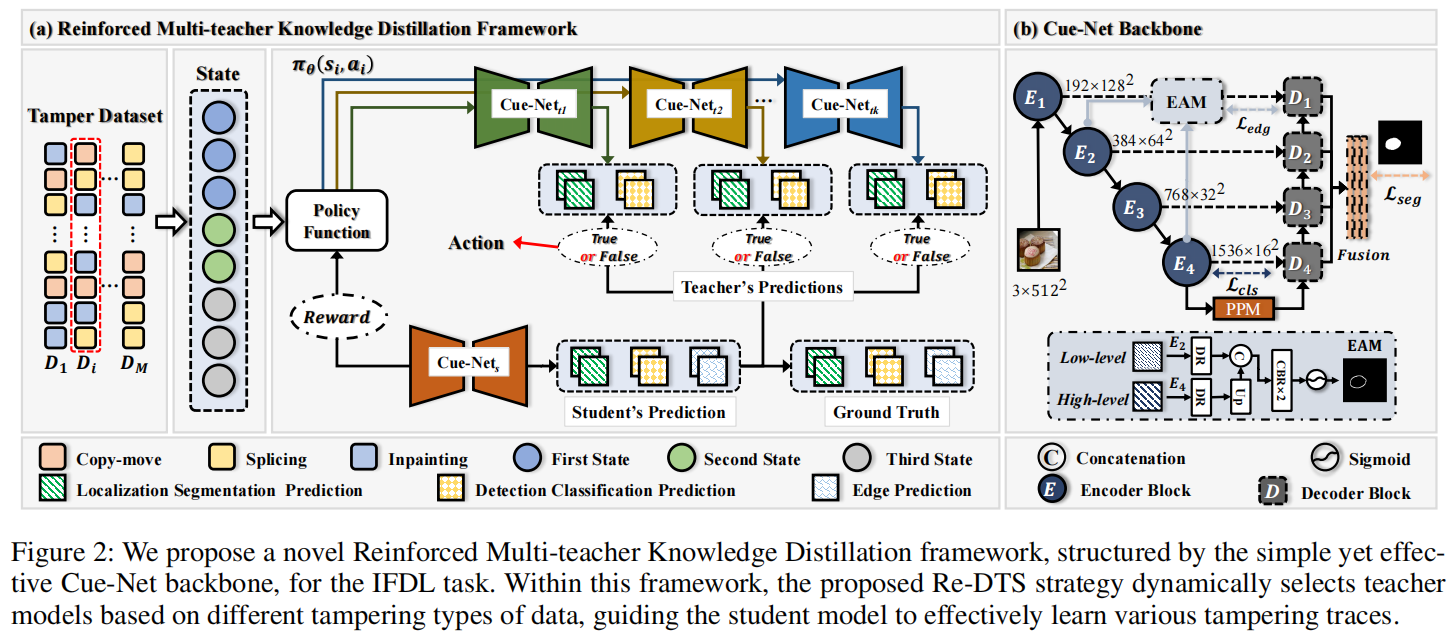
发表于AAAI2025,该框架的核心是Re-DTS策略,动态选择最合适的教师模型,将专业知识转移到学生模型。这一策略增强了学生模型处理各种篡改痕迹的能力,并提高了IFDL性能,将强化学习引入到了图像篡改检测。
2025年5月12日
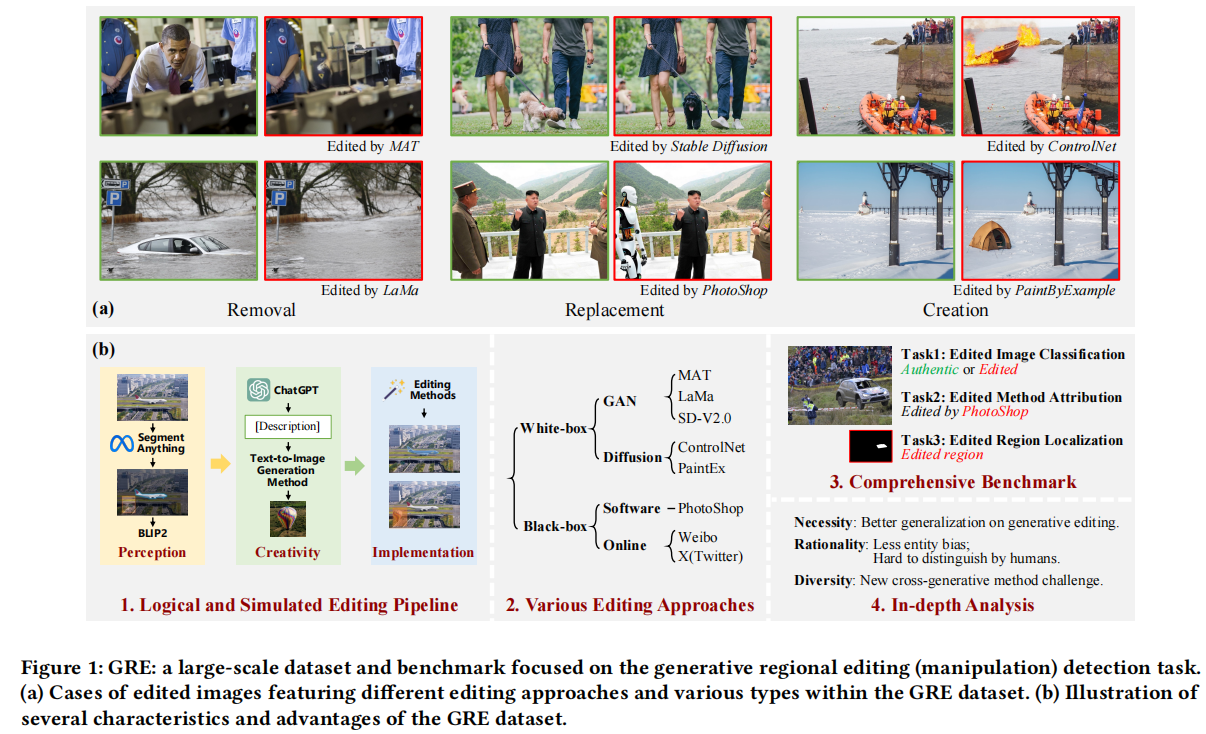
发表于ACMMM 2025,提出了基于图像编辑技术的新数据集。
2025年3月27日
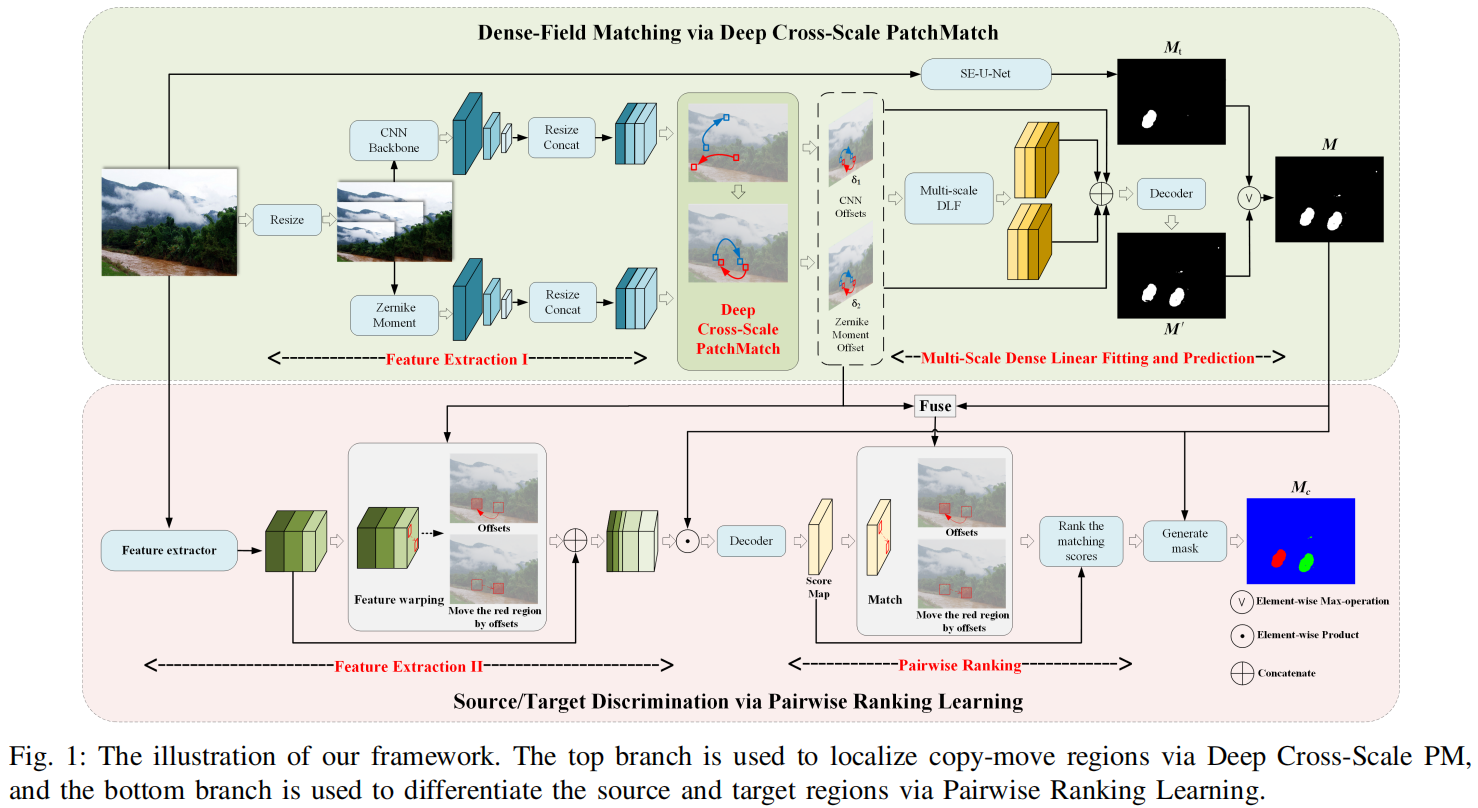
发表于TIP 2024,图像复制-移动伪造检测方向的图像篡改检测方法。
2025年3月10日
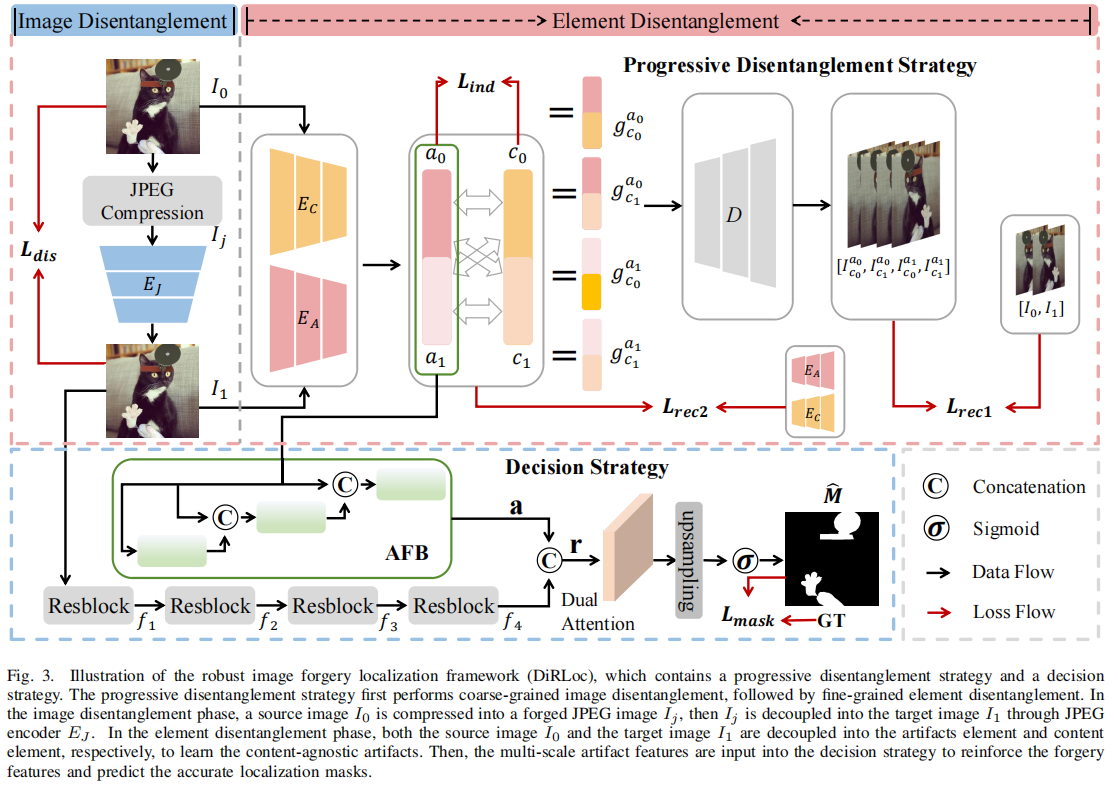
发表于TDSC2024,针对JPEG压缩导致的性能下降,使用解纠缠的方法,分离出jpeg压缩对篡改痕迹的影响,提出了一种鲁棒的图像伪造定位框架。
2025年3月10日
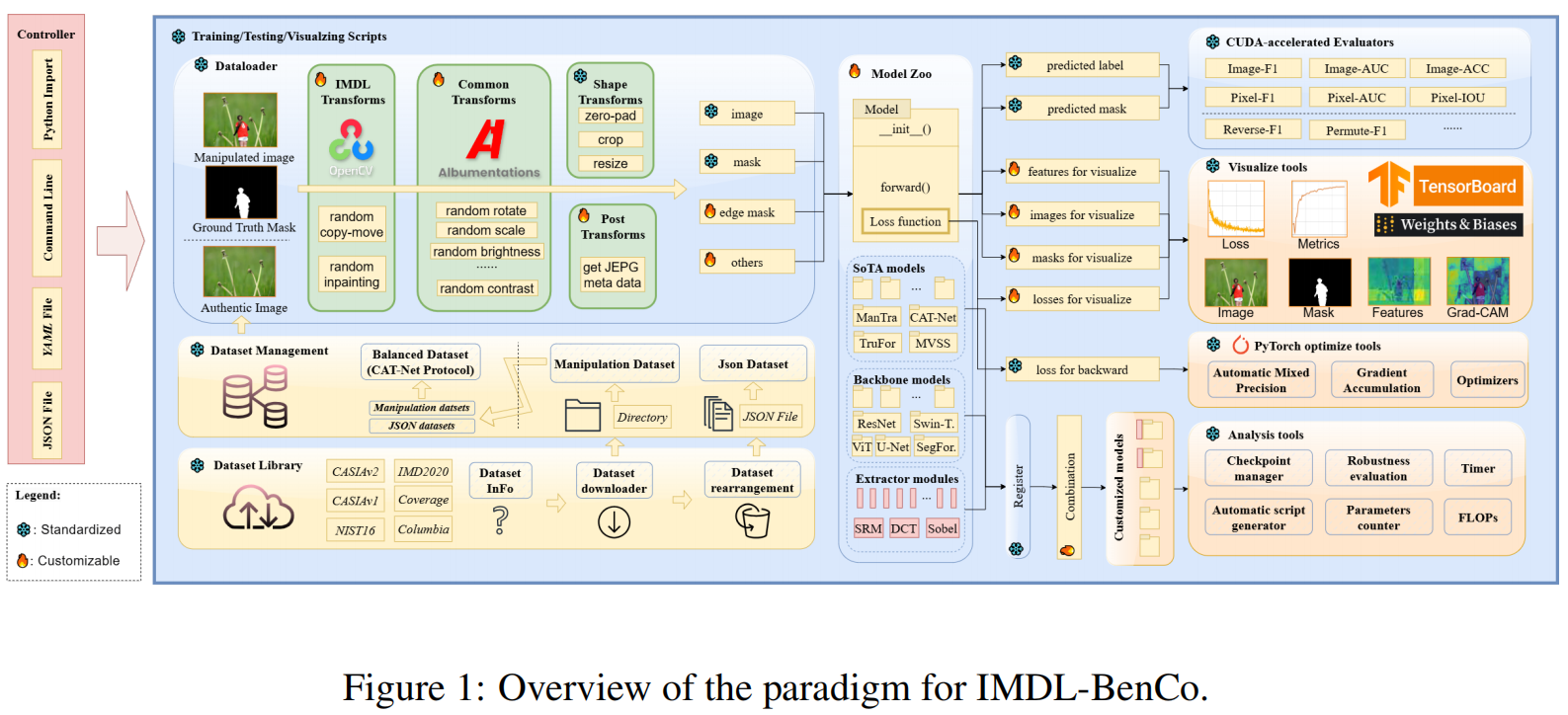
发表于NeurIPS 2024,因为图像篡改检测没有统一的标准,所以构建一个全面的基准,并且设计了一个框架将部分sota网络集成:Mantra-Net,MVSS-net,CAT-Net,ObjectFormer,PSCC-Net,NCL-IML,Trufor和IML-ViT。
2025年3月6日
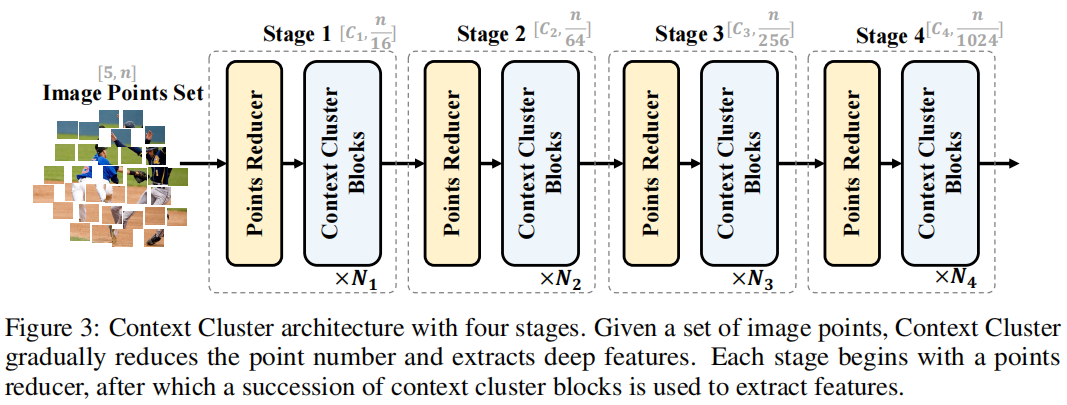
发表于ICLR2023,将图像视为一组无组织的点,并通过简化的聚类算法提取特征。具体地说,每个点都包括原始特征(如颜色)和位置信息(如坐标),并采用简化的聚类算法对深度特征进行分层分组和提取。
2025年2月24日
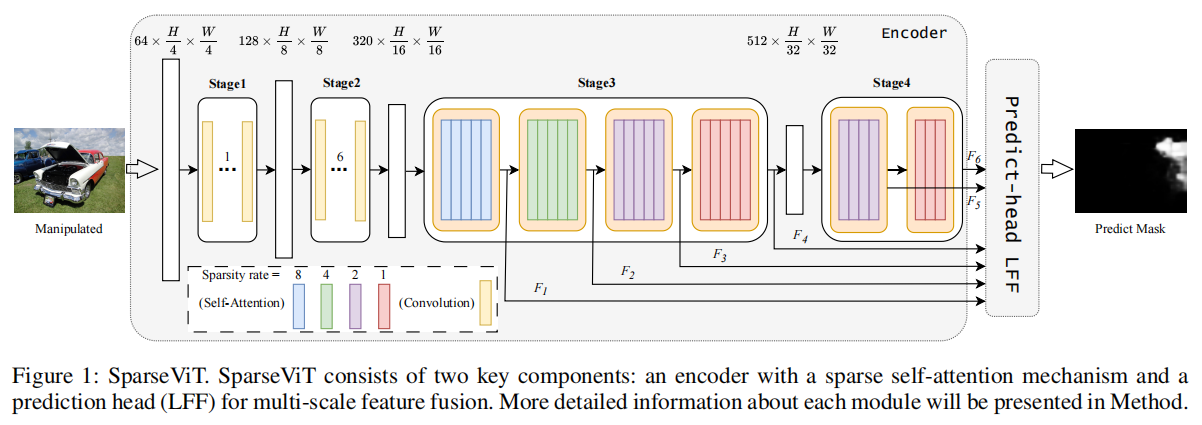
发表于AAAI2025,SparseViT认为图像篡改检测应该是非语义的,非语义特征与上下文无关,且对篡改敏感。也就是说,在图像中,除非发生篡改,否则它们在各个补丁之间是一致的,而图像块之间的稀疏和离散交互足以提取非语义特征,非语义特征由于其局部独立性,可以通过稀疏编码实现全局交互。
2025年2月19日
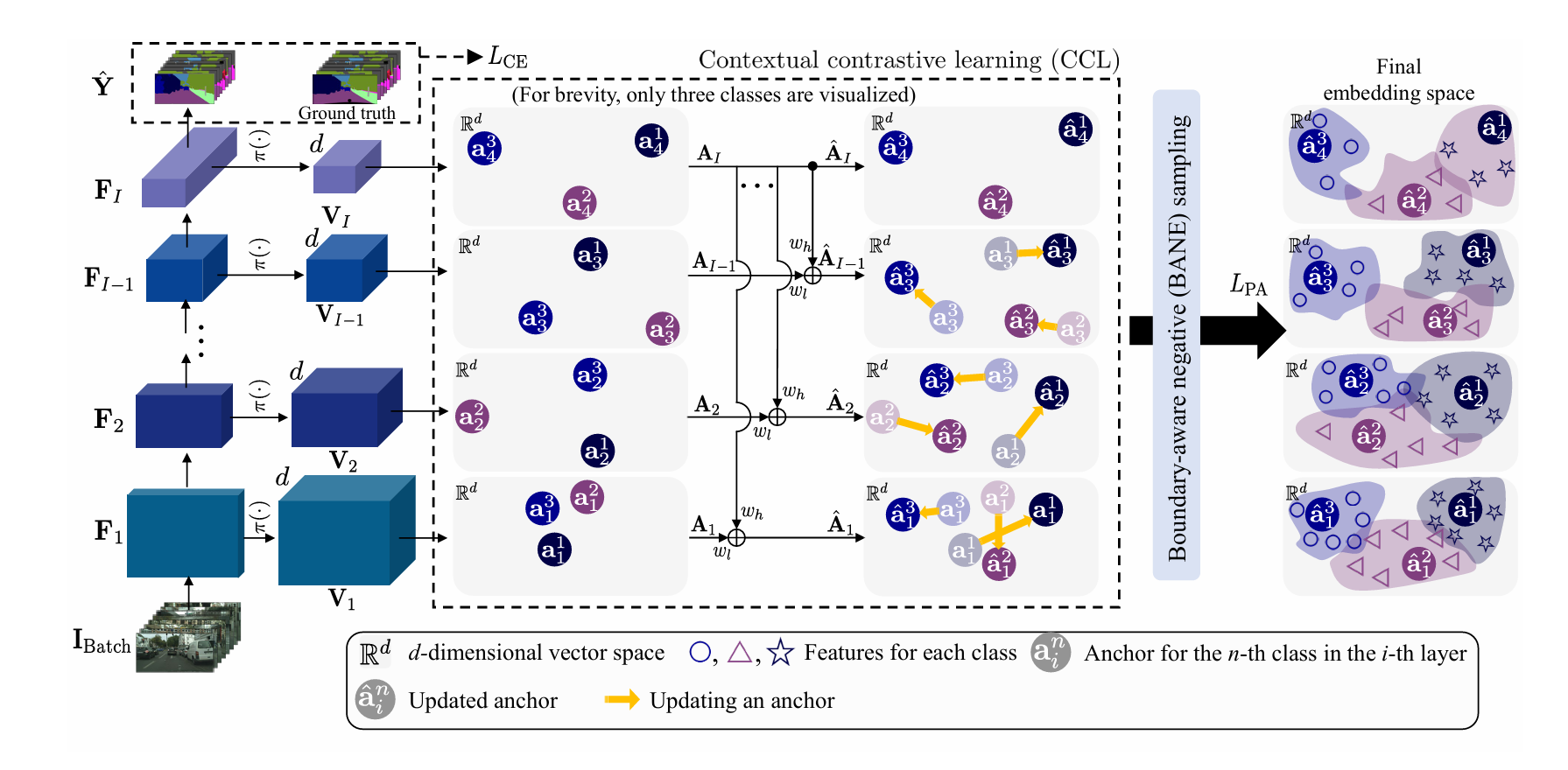
发表于CVPR2024,该论文面向语义分割任务中不准确的分割边界,提出了Contextrast,即设计了一个基于INfoNCE损失的新损失函数,以保证在不同尺度下的特征(不同类别的平均特征)的空间关系保持一致,还提出了基于边界引导的负样本挖掘方法,旨在提高负样本的质量。(代码未公布)
2025年2月17日
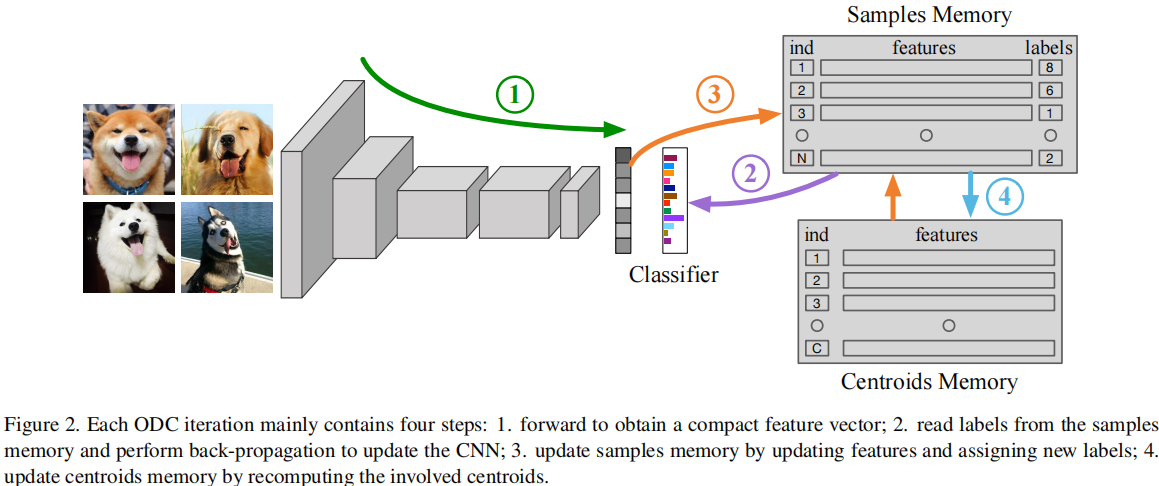
发表于CVPR2020,其提出了在线深度聚类的方法,即设计并维护了两个动态内存模块,即用于存储样本标签和特征的样本内存,以及用于质心进化的质心内存,将突然的全局聚类分解为稳定的内存更新和批量标签重新分配。
2025年2月17日
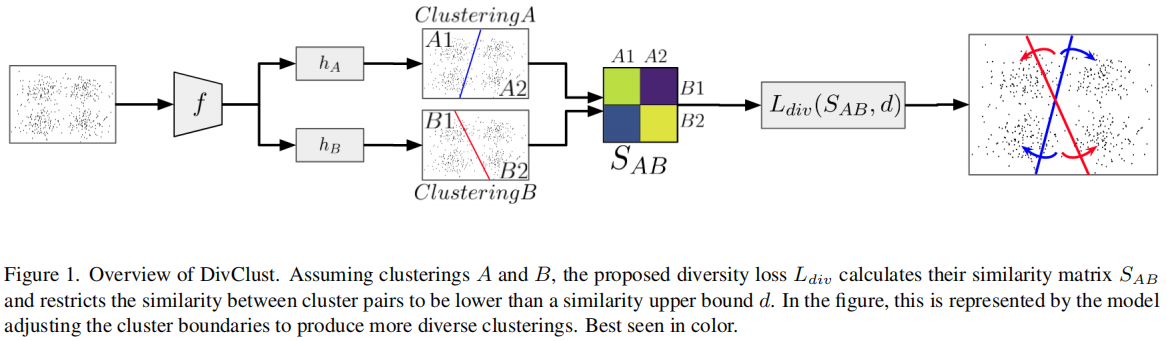
发表于CVPR2023,共识聚类是一种无监督的集成聚类方法,旨在通过多次重采样和聚类分析来评估聚类结果的稳定性,从而确定数据集中最优的聚类数目(k值)及其成员结构。该论文提出了DivClust,一种多样性控制损失,可以纳入现有的深度聚类框架,以产生具有所需多样性程度的多个聚类。
2025年2月16日
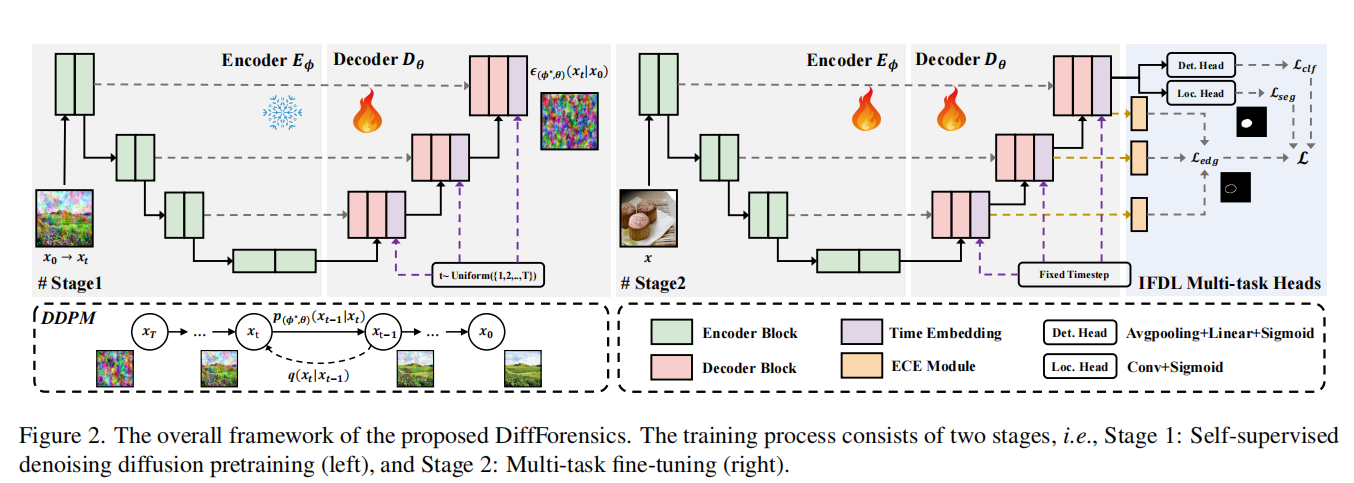
发表于CVPR2024,两阶段的训练过程,该框架包括自监督去噪扩散的训练前阶段和多任务微调阶段,提出了一种新的边缘提示增强模块,该模块集成在多个尺度的解码器中,以增强被篡改的边缘痕迹从粗到细。
2025年1月15日
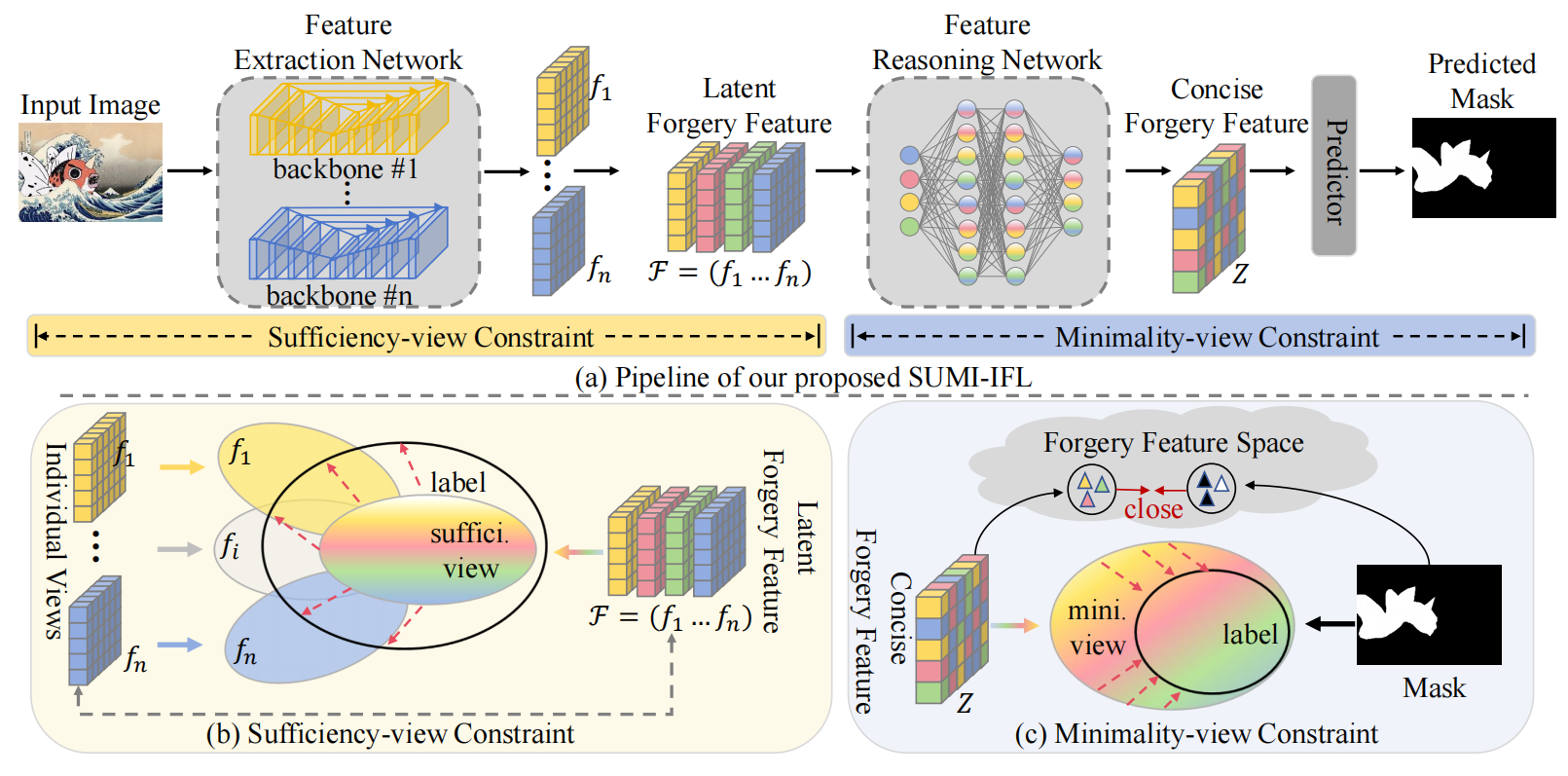
发表于aixiv,使用信息瓶颈理论完成图像篡改任务,没和NP++、IFL-VIT比较。
2025年1月15日
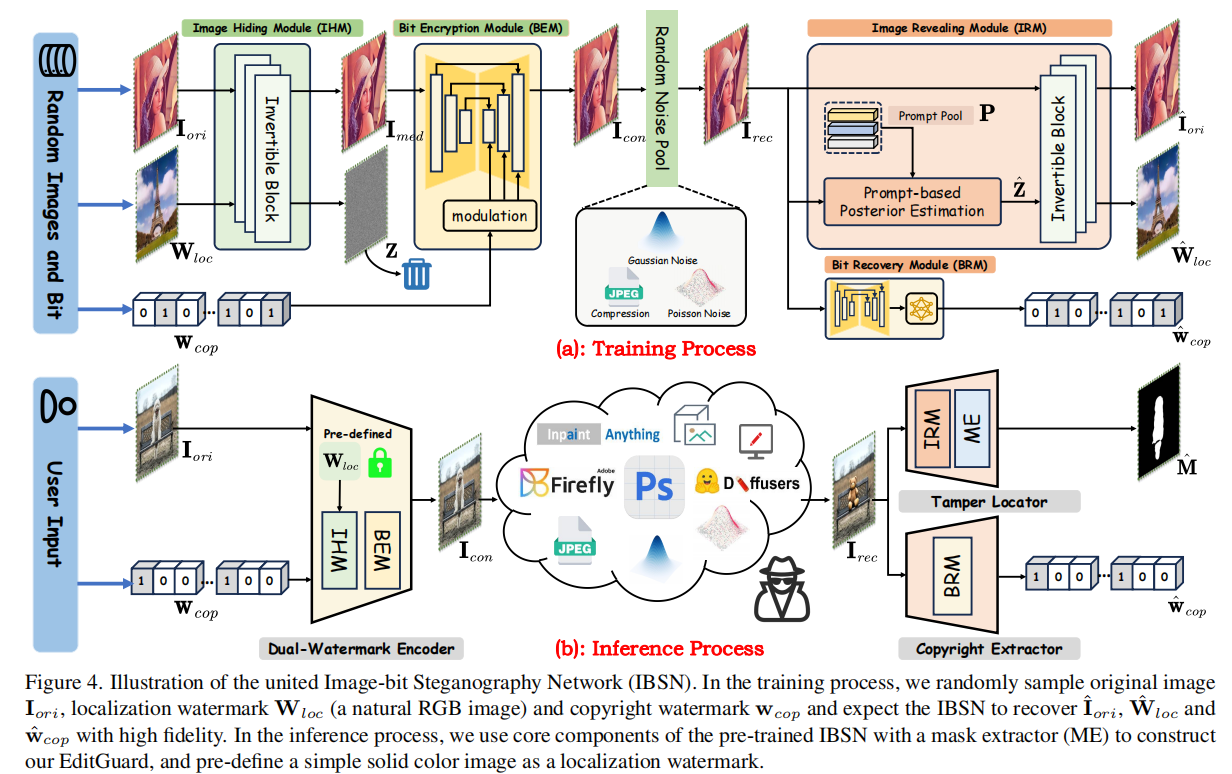
发表于CVPR2024,将版权水印和图像篡改主动保护两个任务联合起来。
2025年1月13日
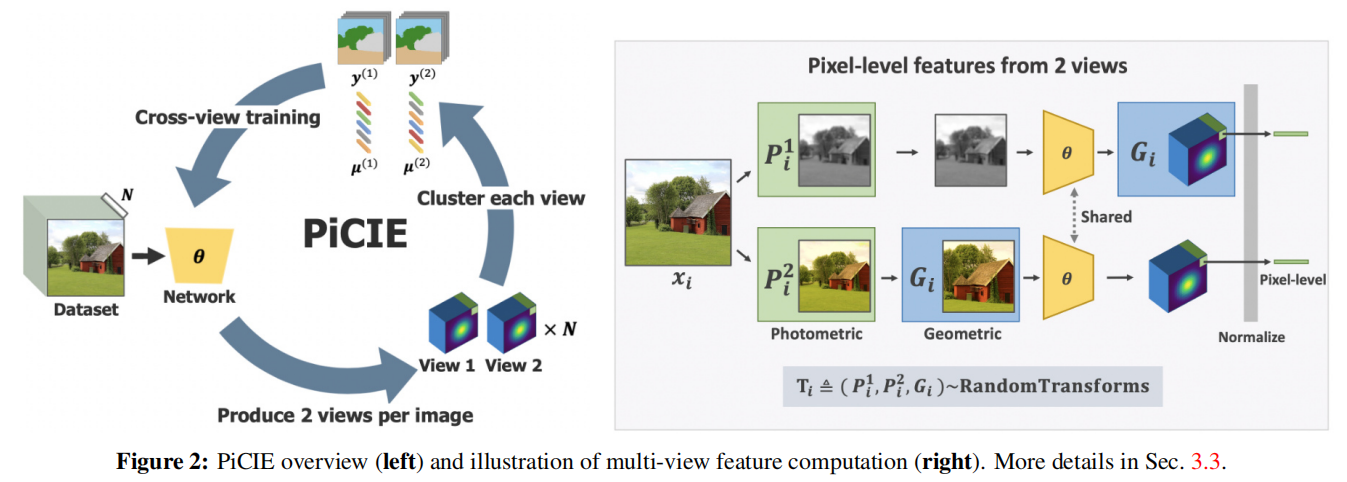
发表于CVPR2021,无监督语义分割,使用聚类伪标签和交叉熵损失,同时使用数据增强,利用增强不变性,提高模型泛化性,使模型不关注噪声。
2025年1月8日
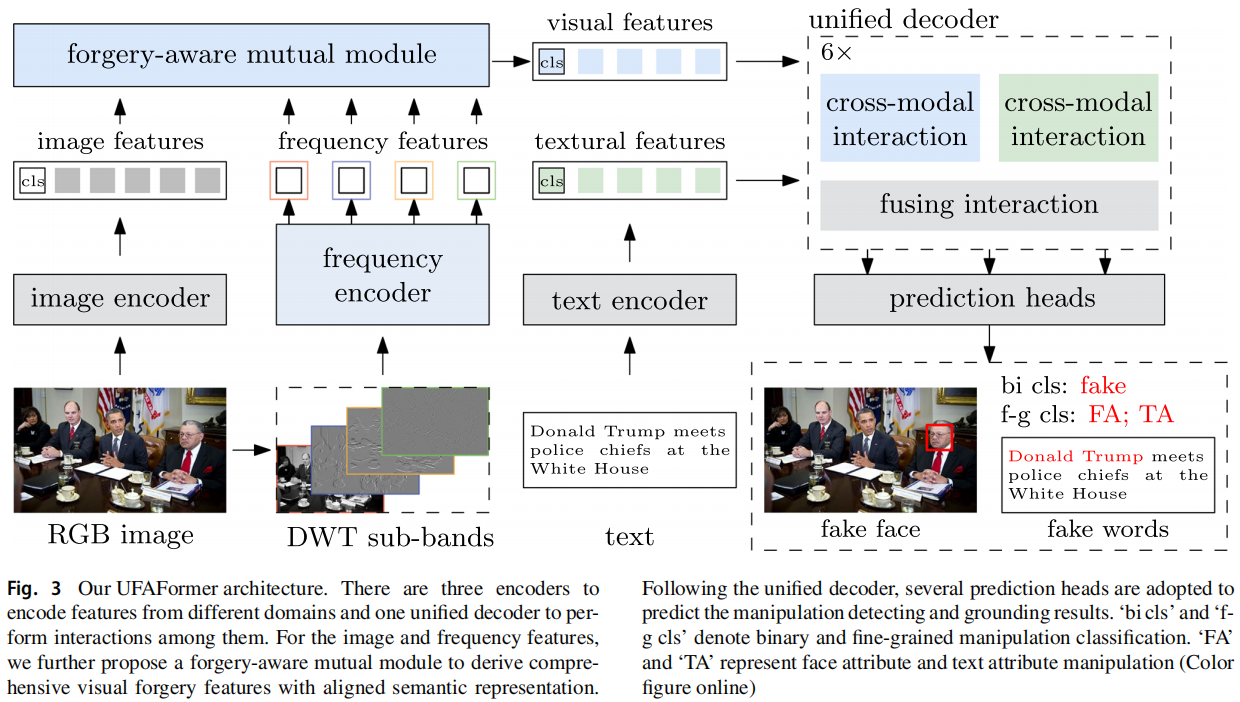
发表于IJCV 2024,多模态的图像篡改检测。
2024年10月21日
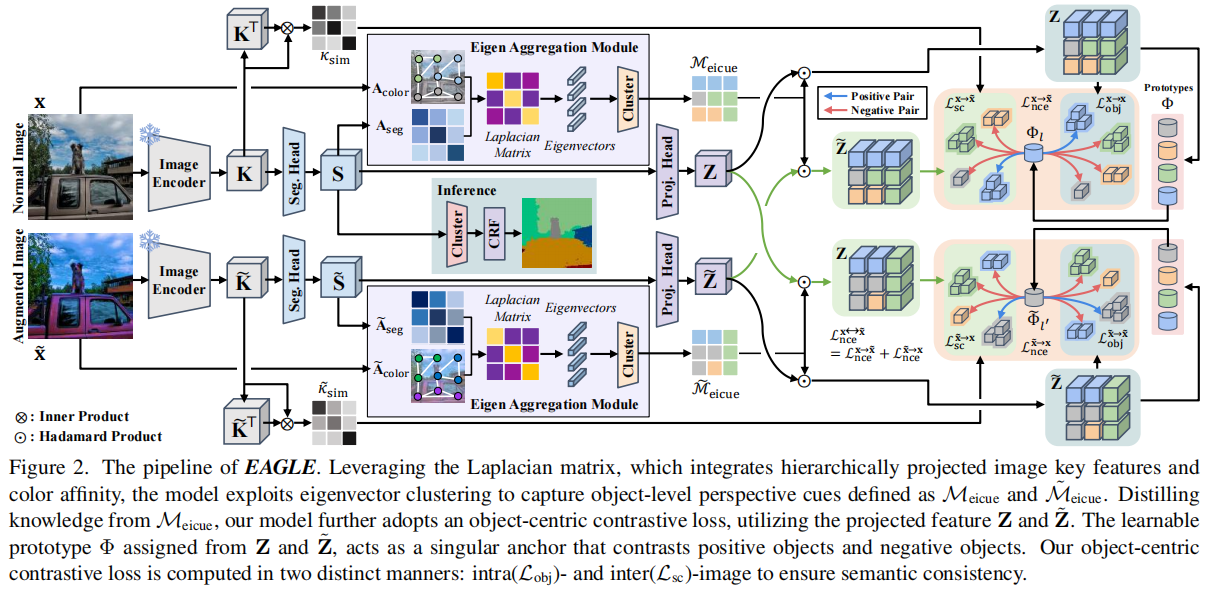
发表于CVPR2024。
2024年10月8日
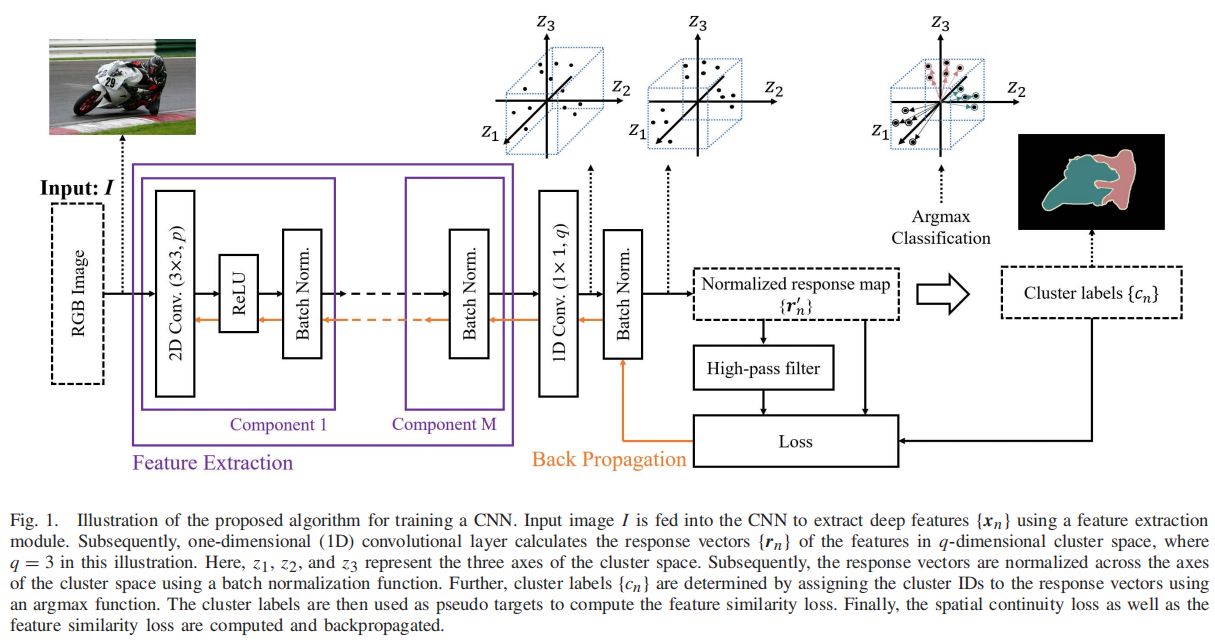
发表于TIP 2020,无监督语义分割和可微聚类方法。
2024年10月7日
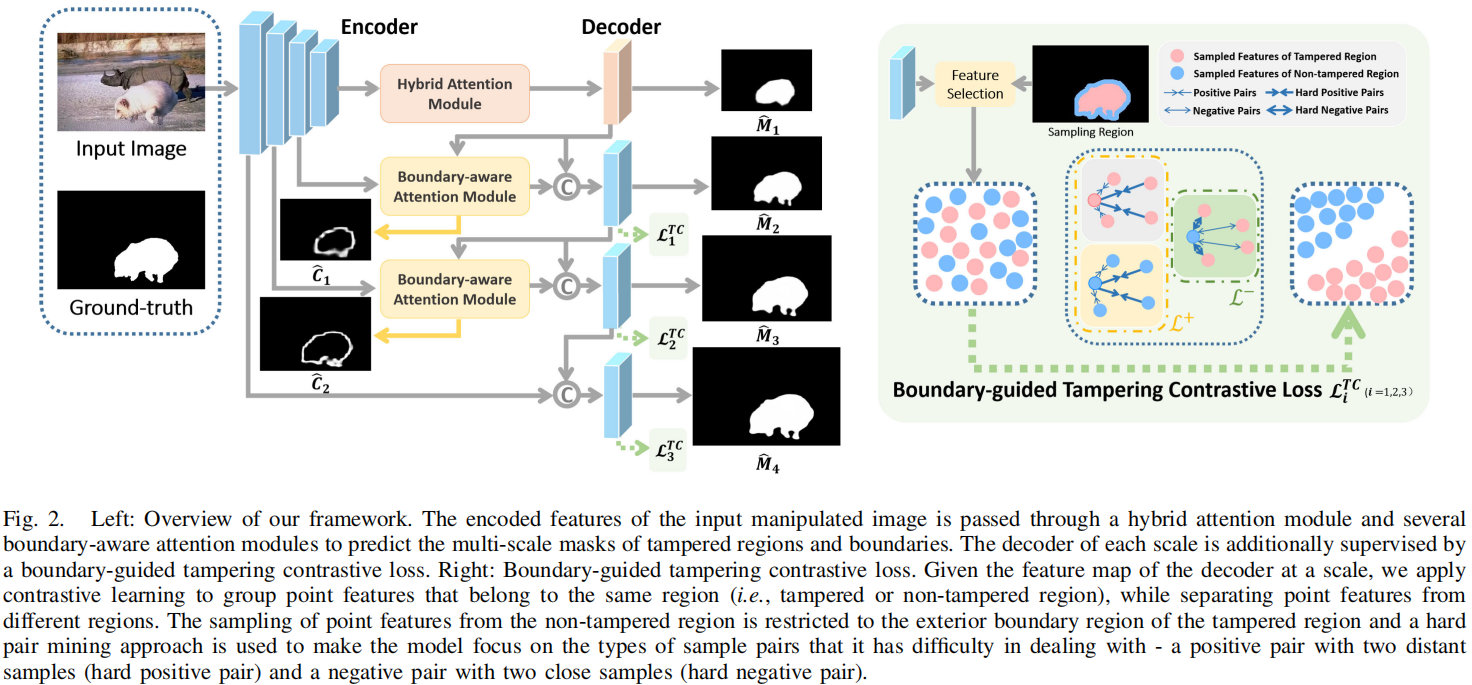
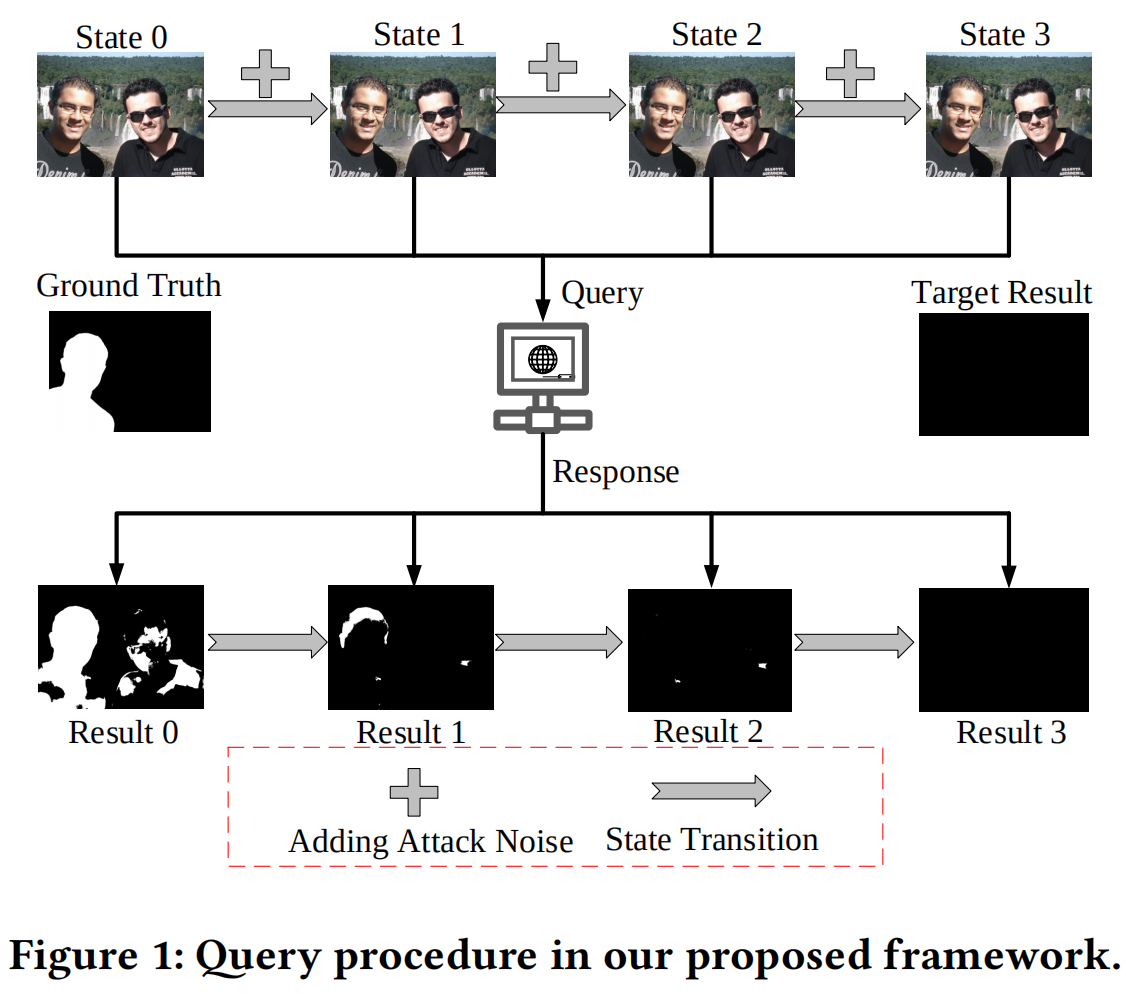
发表于TIFS2024,被篡改区域的边界是分离被篡改和未被篡改像素的关键位置,在这项工作中,我们提出了一种图像操作检测的边界感知方案,其中我们引入了充分利用篡改区域的边界信息,并从注意和特征学习两个角度实现了我们的方案。
现有问题:被篡改区域的边界是分离被篡改和未被篡改像素的关键位置。然而,如何利用这些边界信息来提高检测被篡改图像区域的性能仍有待探索。
解决方案:
在这项工作中,我们提出了一种图像操作检测的边界感知方案,其中我们引入了充分利用篡改区域的边界信息,并从注意和特征学习两个角度实现了我们的方案。首先,为了进一步增强操作定位,我们鼓励该模型关注一个被篡改区域周围的边界,其中经常存在非自然的混合。其次,受对比学习的启发,我们寻求学习一个特征空间,即篡改区域内的点远离篡改区域边界附近的非调和区域点,以获得更强大的特性来定位篡改区域。
具体情况
在注意方面,在我们的框架的解码层中,我们提出了一种新的基于交叉注意的边界感知模块,旨在提取图像中被篡改区域的边界,从而使模型进一步集中于被篡改区域的边界。特别是,边界感知注意模块利用跳连编码特征与前一层解码特征的相关性,提取被篡改区域的边界,进一步用于生成图像篡改定位的掩模。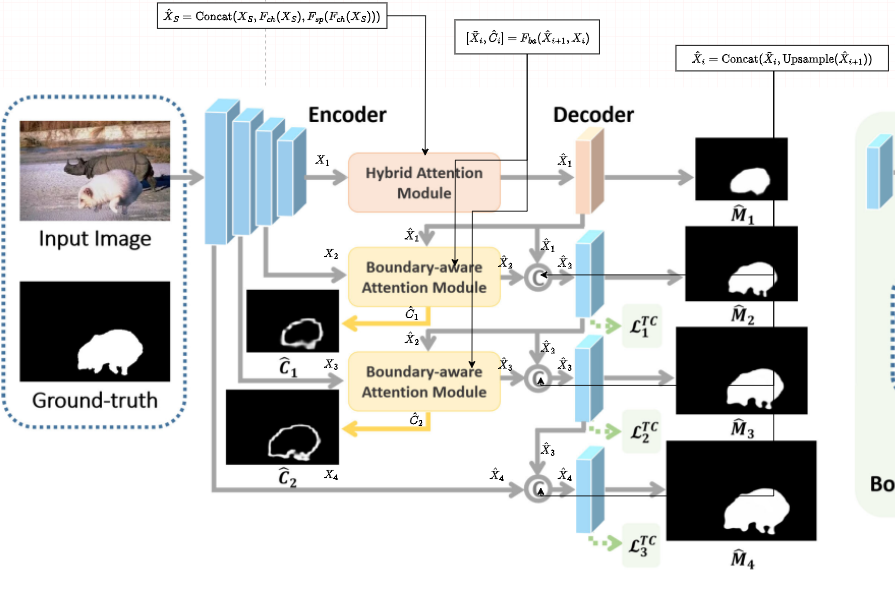 在特征学习方面,我们提出的模型是基于一个典型的编解码器架构及其特征学习监督由一个新颖的对比目标函数[16],[22],[23],表示为边界引导篡改对比损失,为了推动分开特征采样的篡改和非篡改区域,从而学习更多的区别特征表示。为此,我们采用边界引导的采样策略来收集负训练对,其中我们在被篡改区域的边界周围采样负样本,而不是整个非被篡改区域。该采样方案不仅鼓励模型关注存在非自然混合的边界区域,而且减轻了未篡改区域内巨大变化引起的干扰(见图1中的可视化特征)。
在特征学习方面,我们提出的模型是基于一个典型的编解码器架构及其特征学习监督由一个新颖的对比目标函数[16],[22],[23],表示为边界引导篡改对比损失,为了推动分开特征采样的篡改和非篡改区域,从而学习更多的区别特征表示。为此,我们采用边界引导的采样策略来收集负训练对,其中我们在被篡改区域的边界周围采样负样本,而不是整个非被篡改区域。该采样方案不仅鼓励模型关注存在非自然混合的边界区域,而且减轻了未篡改区域内巨大变化引起的干扰(见图1中的可视化特征)。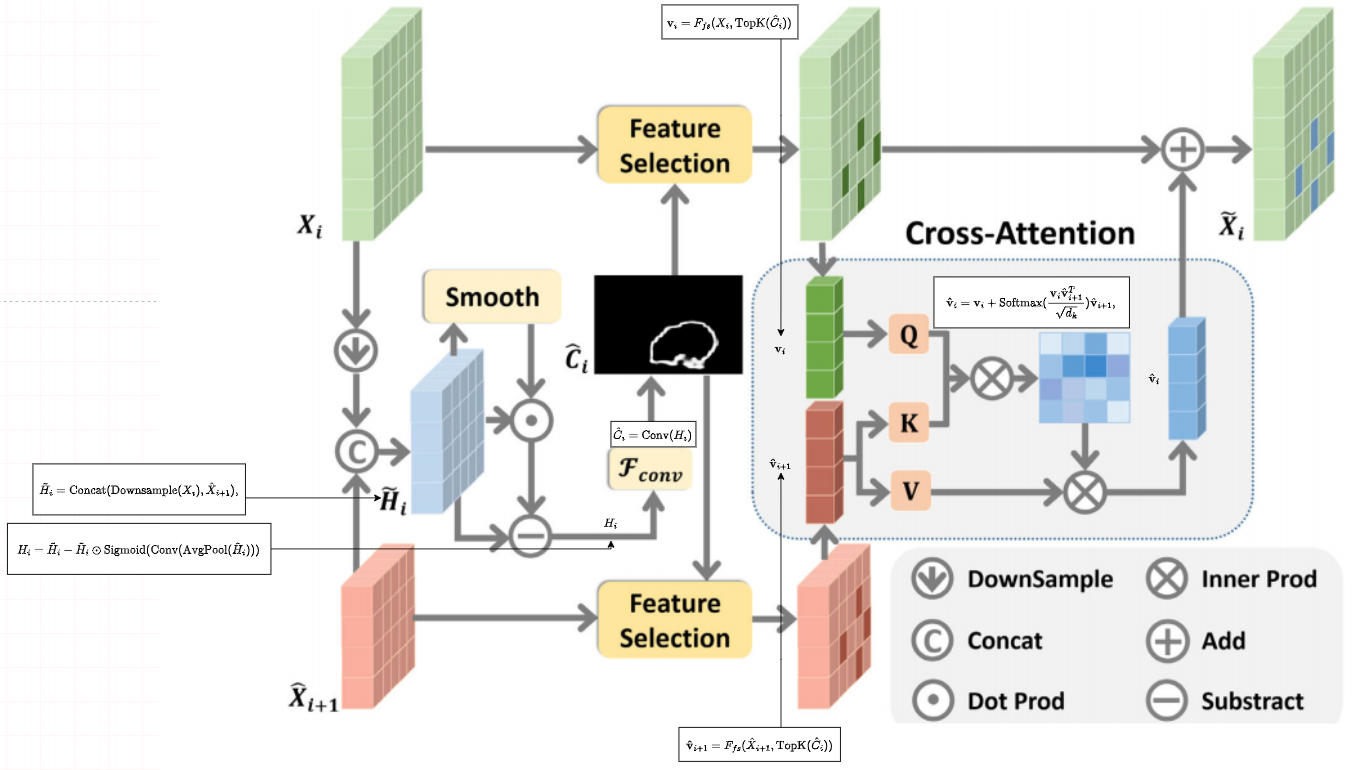

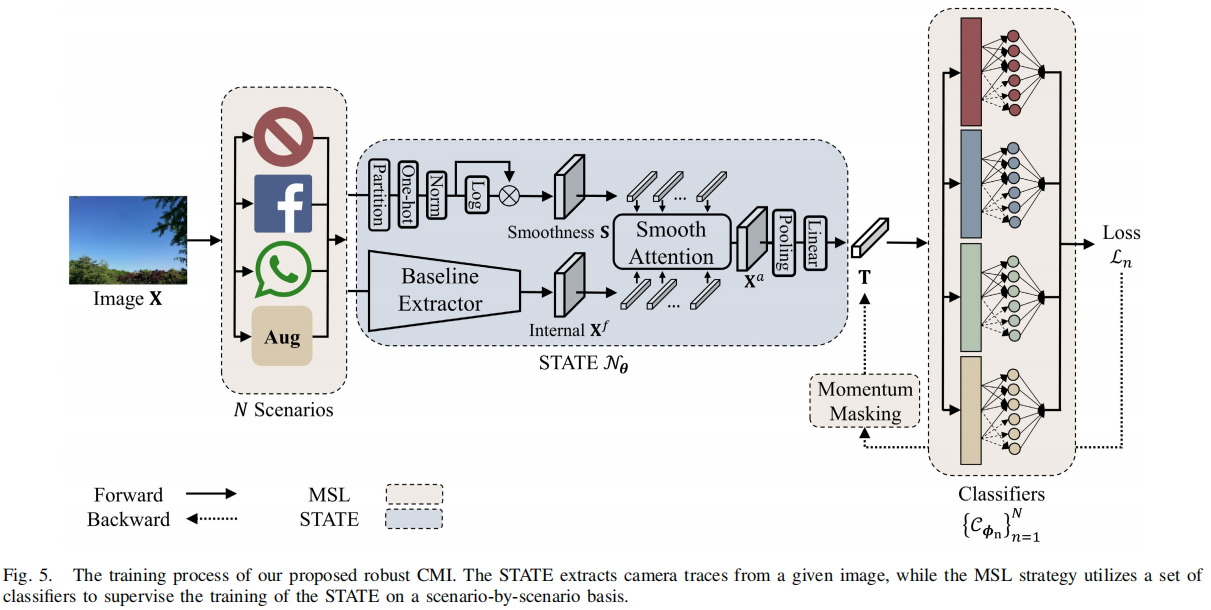
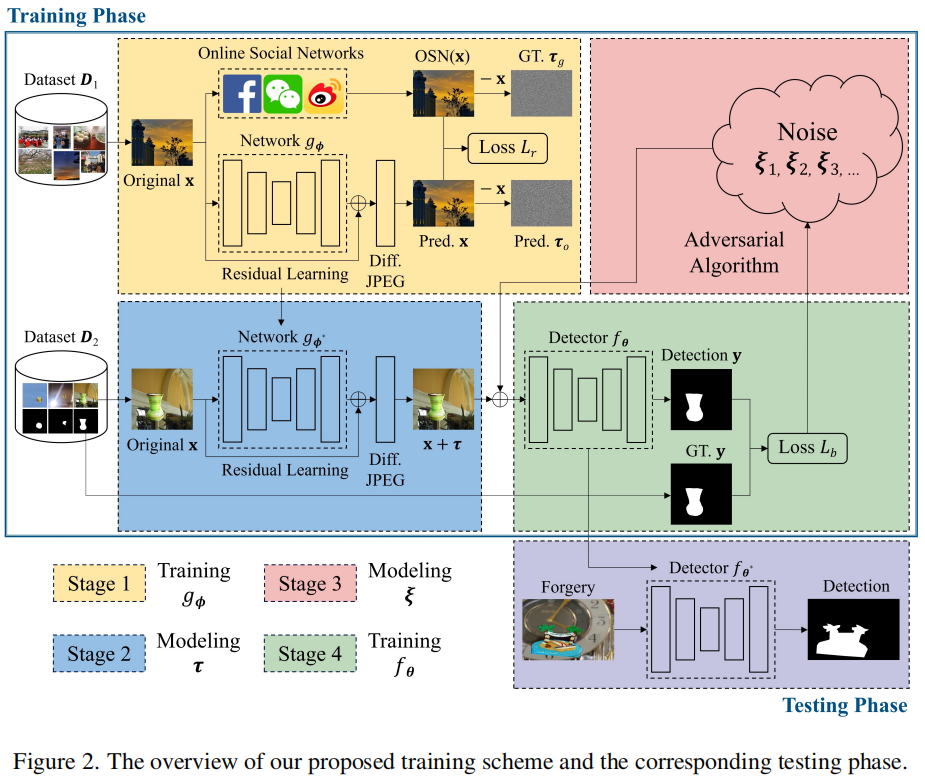
发表于TIFS2023,随着互联网的蓬勃发展,在线社交网络(OSNs, online social networks)已成为图像共享和传输的主导渠道,但OSN传输下所有现有算法的性能都会严重下降,尤其是WeChat、QQ、Telegram和Dingding。为了减轻OSN的负面影响,在本工作中,我们提出了一种新的相机轨迹提取方法,该方法有望对各种OSN平台的传输具有鲁棒性。
2024年9月2日
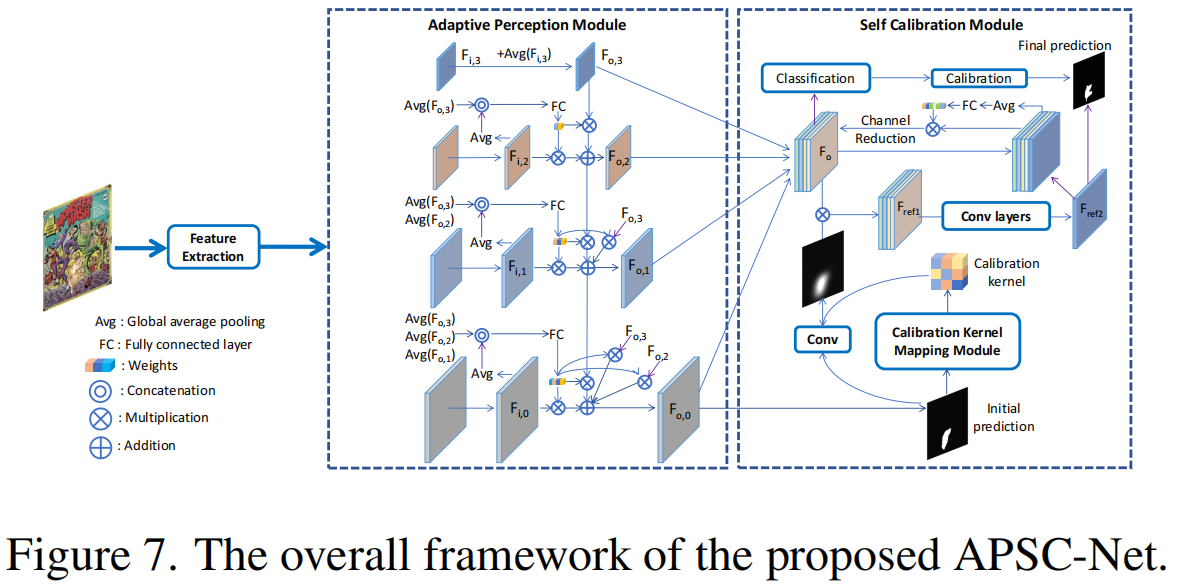
发表于CVPR2024型,CAAA可以像素级自动和精确地注释大量的人工伪造的图像,进一步提出了一种新的度量QES,以方便不可靠注释的自动过滤。
2024年8月26日
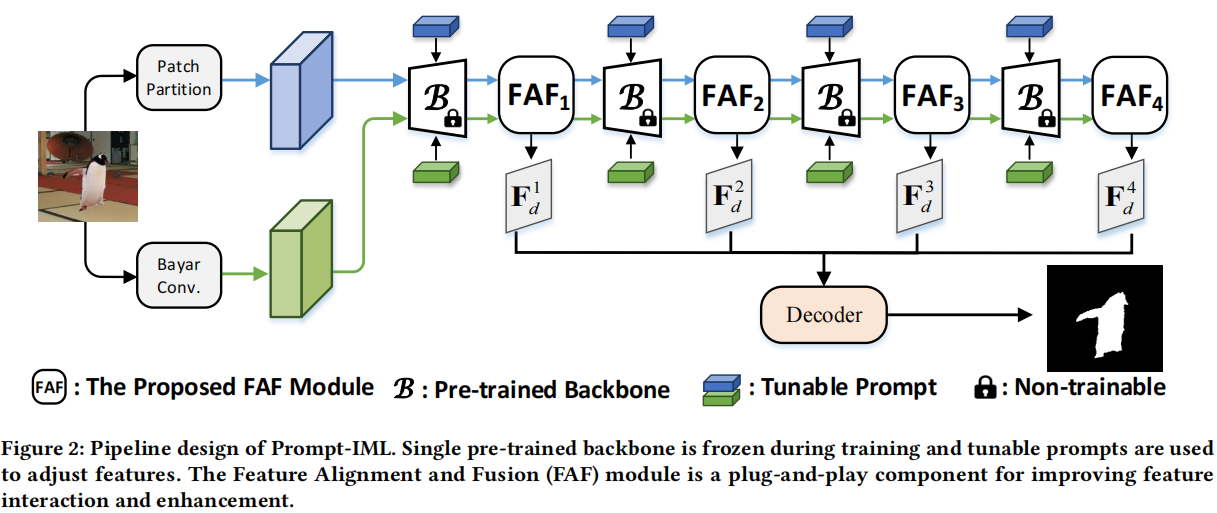
发表于ACMMM2024,针对IML任务中公共训练数据集的稀缺,通过采用可调提示来利用预训练模型的丰富先验知识,即Prompt-IML框架,即插即用的特征对齐和融合模块。
现有问题:IML任务中公共训练数据集的稀缺直接阻碍了模型的性能。
解决方案:
提出了一个Prompt-IML框架,该框架通过采用可调提示来利用预训练模型的丰富先验知识。
具体情况
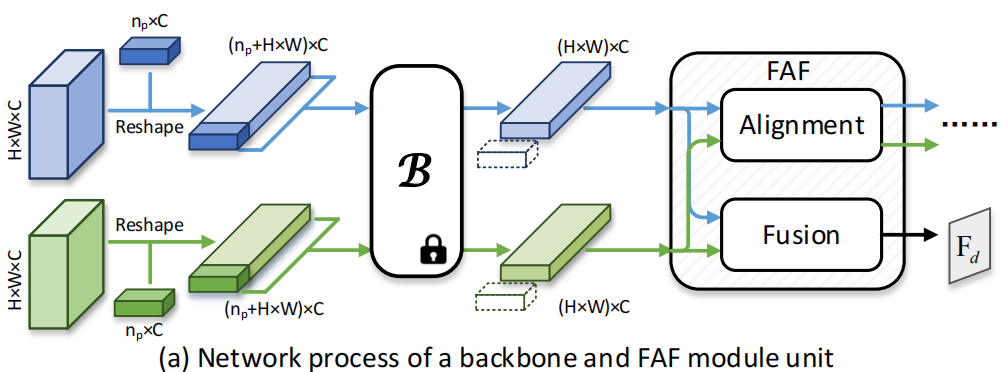
> 通过集成可调提示,从单个预先训练过的主干中提取和调整多视图特征,从而保持性能和鲁棒性 > 特征对齐和融合的FAF模块
> 特征对齐和融合的FAF模块

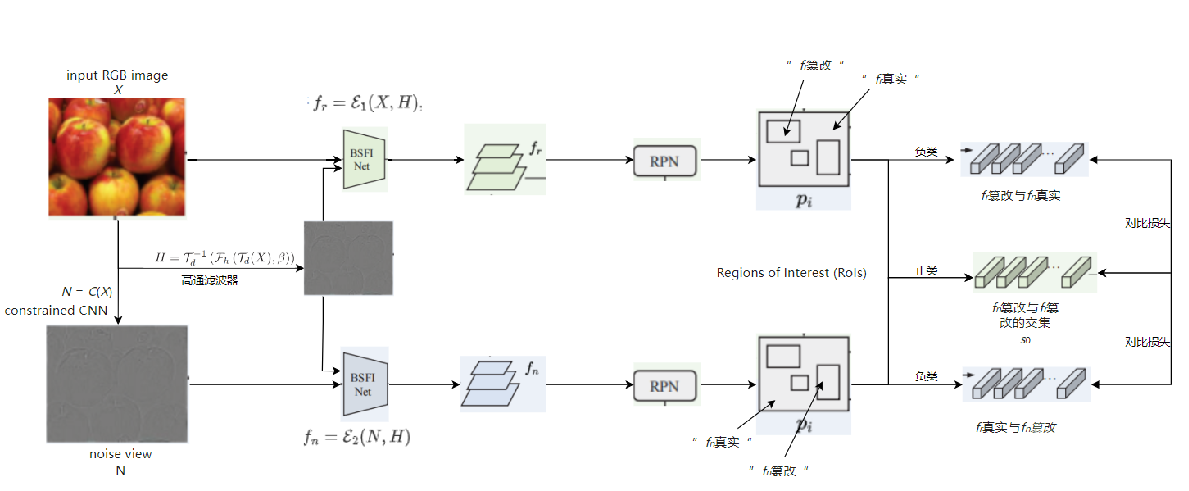
发表于CVPR2024,集成三个视图的UnionFormer框架,一个调节不同尺度上空间一致性的篡改特征提取网络BSFI-Net。
现有问题:以往的方法主要利用为高级视觉任务设计的深度卷积神经网络作为特征编码器或直接连接来自不同层的特征,不能充分表示篡改痕迹;目前的高级方法关注于像素或补丁级的一致性,而忽略了对象级的信息,在自然语言提示的引导下,自动生成的伪造部分更有可能表现出对象的不一致。解决方案:设计了专门用于提取取证工件的边界敏感特征交互网络(BSFI-Net, Boundary Sensitive Feature Interaction Network)设计了用于图像操作检测和定位的多视图表示的统一学习transformer框架
具体情况
> cnn-Transformer并发网络 BSFI-Net,该网络在保持边缘灵敏度的同时,促进了两个分支中不同尺度的特征之间的彻底交互。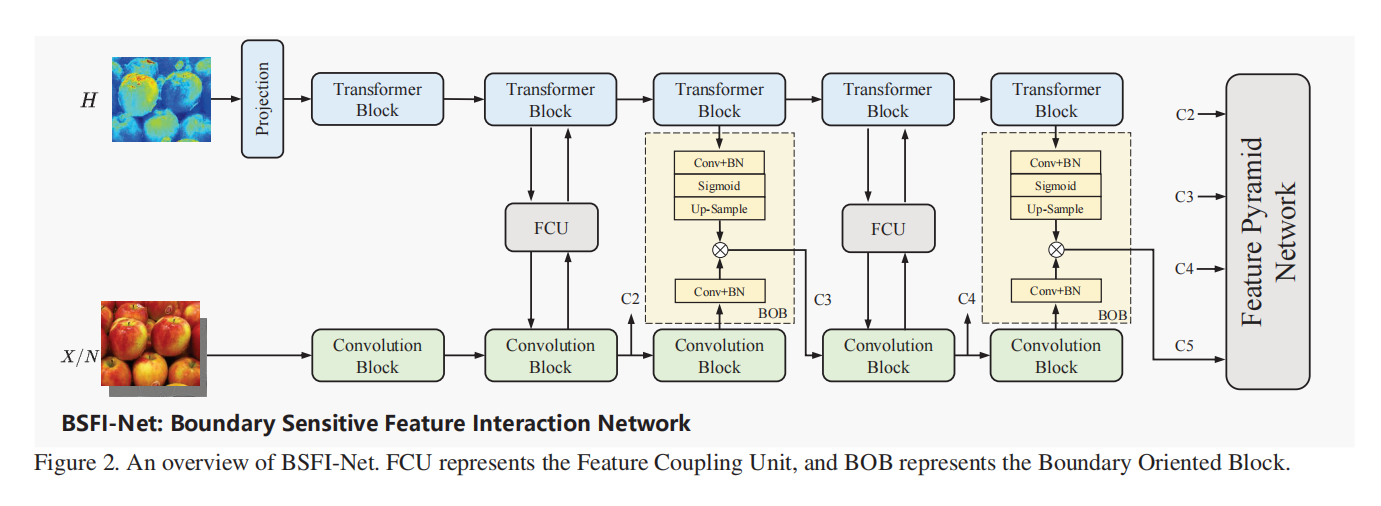 > 采用对比监督来促进两个视图之间的协作
> 采用对比监督来促进两个视图之间的协作
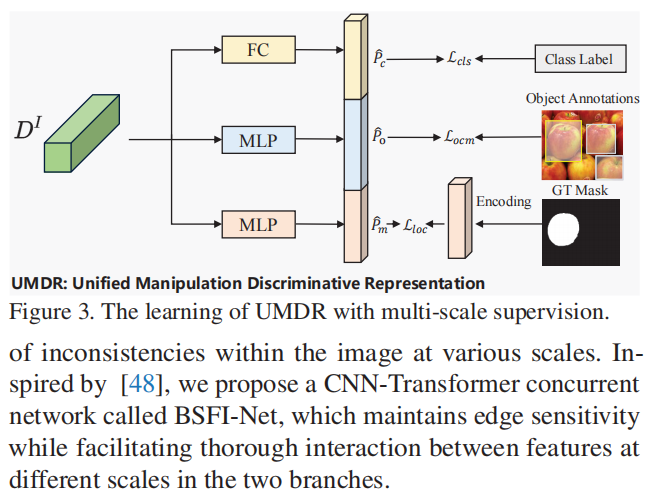
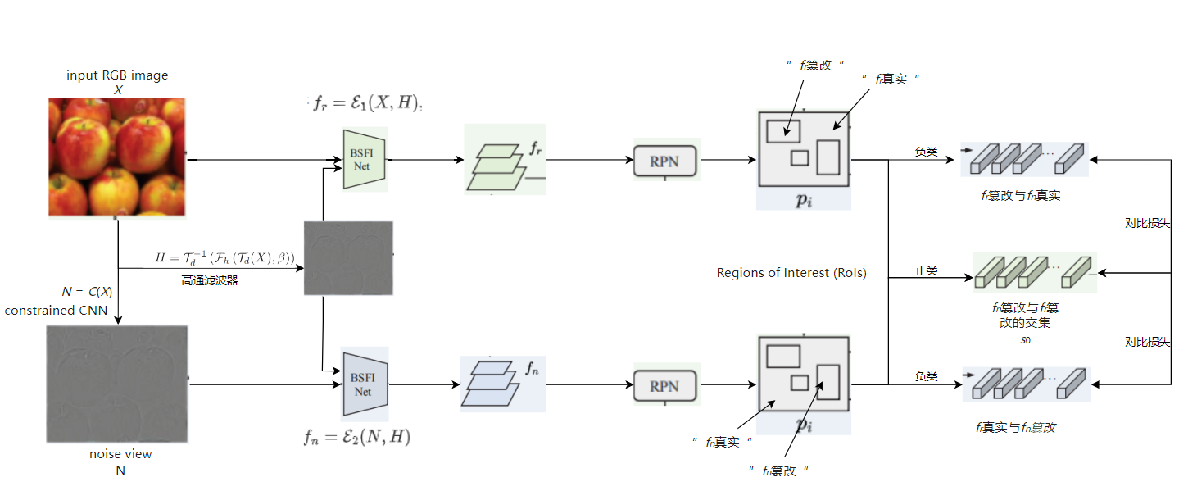 > 统一伪造判别表示,每个篡改判别查询都表示对应建议的三个视图中的篡改线索
> 统一伪造判别表示,每个篡改判别查询都表示对应建议的三个视图中的篡改线索

发表于ICCV2023 将不确定性进行建模。
2024年5月16日
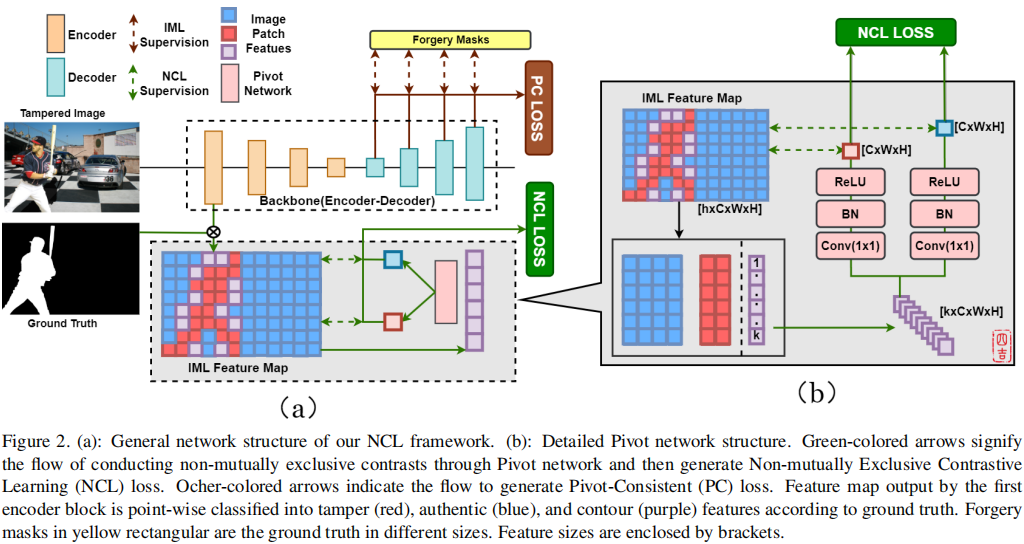
发表于ICCV2023,关注边界的信息,使用边界监督。
2024年5月16日
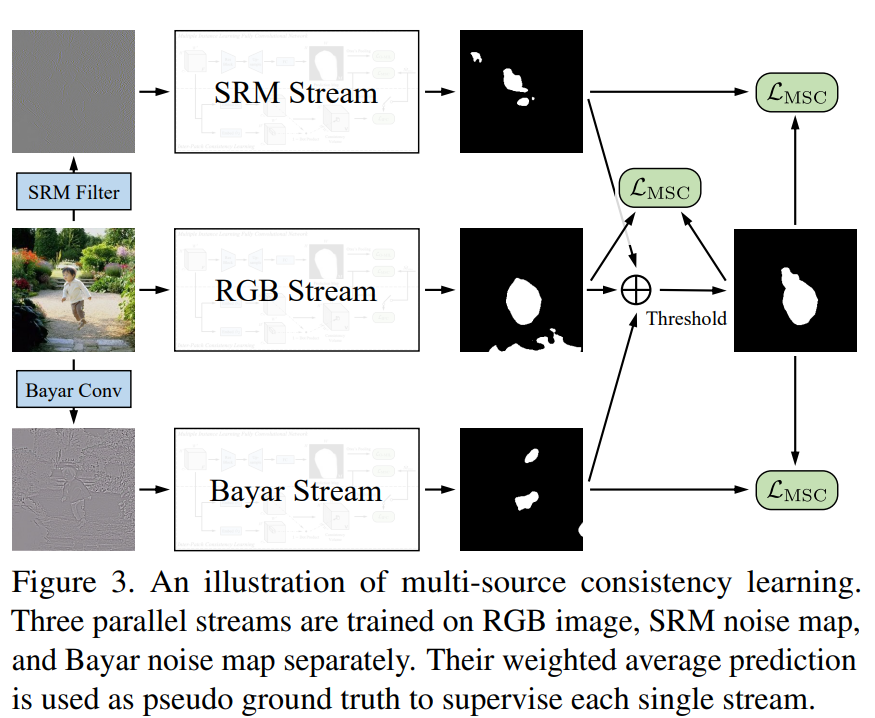
发表于ICCV2023,为弱监督图像篡改检测,具体来说,学习了两个一致性属性,多源一致性(MSC, multi-source consistency)和补丁间一致性(IPC, inter-patch consistency )。MSC利用不同的内容无关信息,并通过在线伪标签生成和细化过程实现跨源学习。IPC执行全局成对补丁关系推理,以发现完整的操作区域。
2024年5月10日
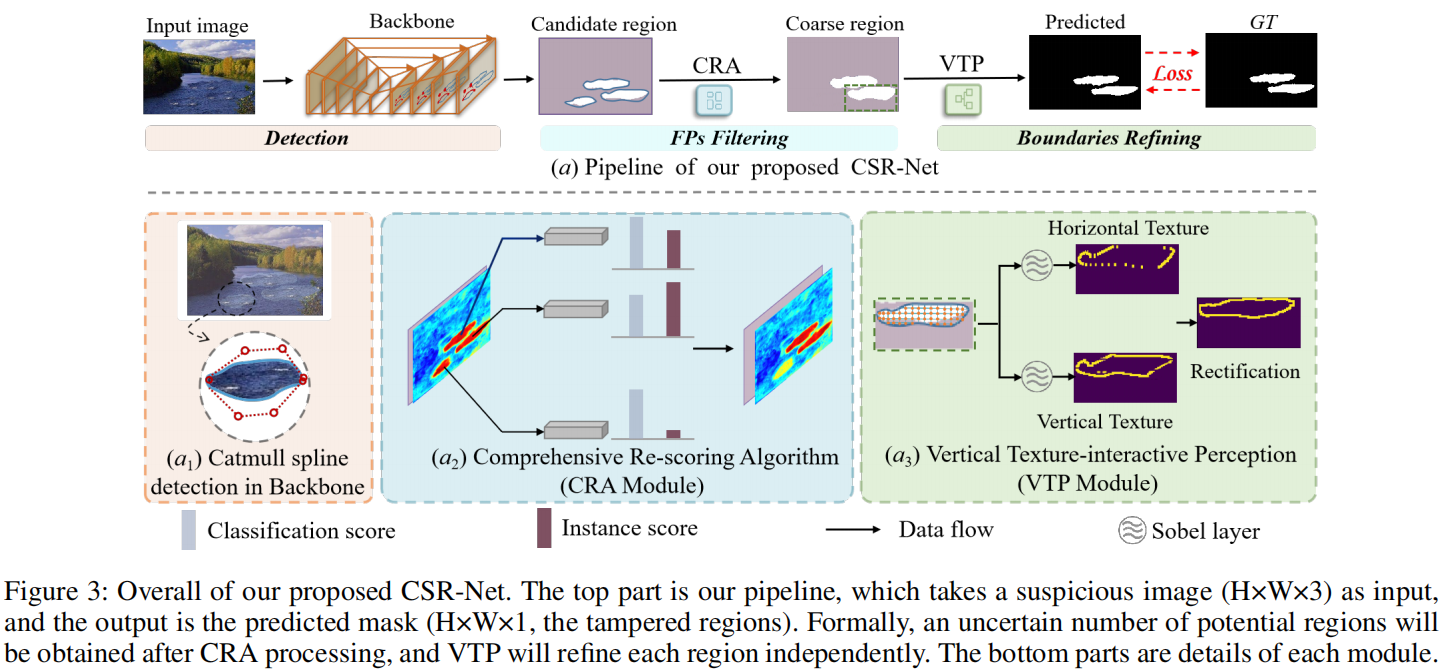
发表于AAAI2024,提出基于CatmullRom样条的回归网络,为了明确抑制假阳性样本和避免不确定性边界,综合再评分算法(CRA,Comprehensive Re-scoring Algorithm),综合评估每个区域的信任分数作为篡改区域,而垂直纹理交互感知(VTP, Vertical Texture-interactive Perception)控制生成更准确的区域边缘。
现有问题:假阳性(FPs)和不准确的边界。
解决方案:
基于CatmullRom样条的回归网络(CSR-Net, CatmullRom Splines-based Regression Network),首次尝试将回归方法引入像素级任务。为了明确抑制假阳性样本和避免不确定性边界,我们设计两个相互互补和强化的组件,即综合再评分算法(CRA,Comprehensive Re-scoring Algorithm),综合评估每个区域的信任分数作为篡改区域,而垂直纹理交互感知(VTP, Vertical Texture-interactive Perception)控制生成更准确的区域边缘。
具体情况
 在本文中,我们精心设计了一个定制的基于CatmullRom样条的回归网络(CSR-Net),并尝试将回归方法引入像素级图像篡改定位(本文中的IFL)。
在本文中,我们精心设计了一个定制的基于CatmullRom样条的回归网络(CSR-Net),并尝试将回归方法引入像素级图像篡改定位(本文中的IFL)。详细地说,与传统的边界盒检测方法相比,我们引入了CatmullRom定位技术,该技术对目标区域控制点的轮廓进行了建模,从而实现了更准确和有效的篡改区域定位。然后,为了抑制FPs(假阳性),设计了综合再评分算法(CRA),我们为每个区域实例重新分配分数,区域实例的综合得分由分类得分(CLS)和实例得分(INS)两部分组成。
此外,我们还提出了一个可学习的区域纹理提取模块垂直纹理交互感知(VTP)来进一步参考边缘。
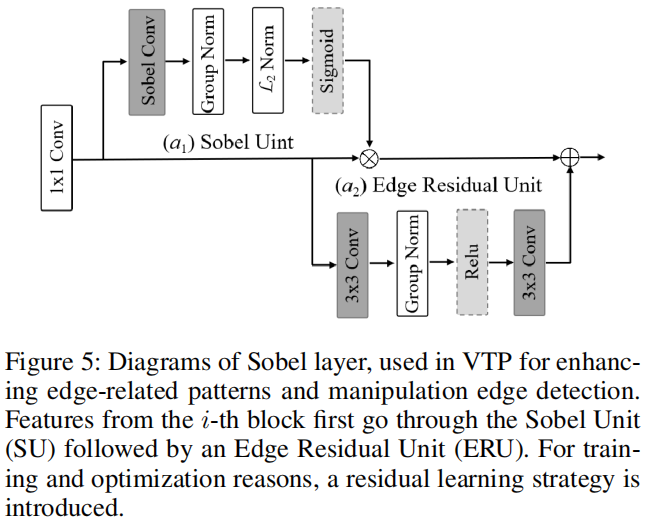 因此,CSRNet可以在不接近FPs的情况下感知所有被篡改的区域,并实现准确的定位。大量的实验表明,CSR-Net优于现有的最先进的方法,不仅在自然图像数据集上,而且在社交媒体数据集上。
因此,CSRNet可以在不接近FPs的情况下感知所有被篡改的区域,并实现准确的定位。大量的实验表明,CSR-Net优于现有的最先进的方法,不仅在自然图像数据集上,而且在社交媒体数据集上。
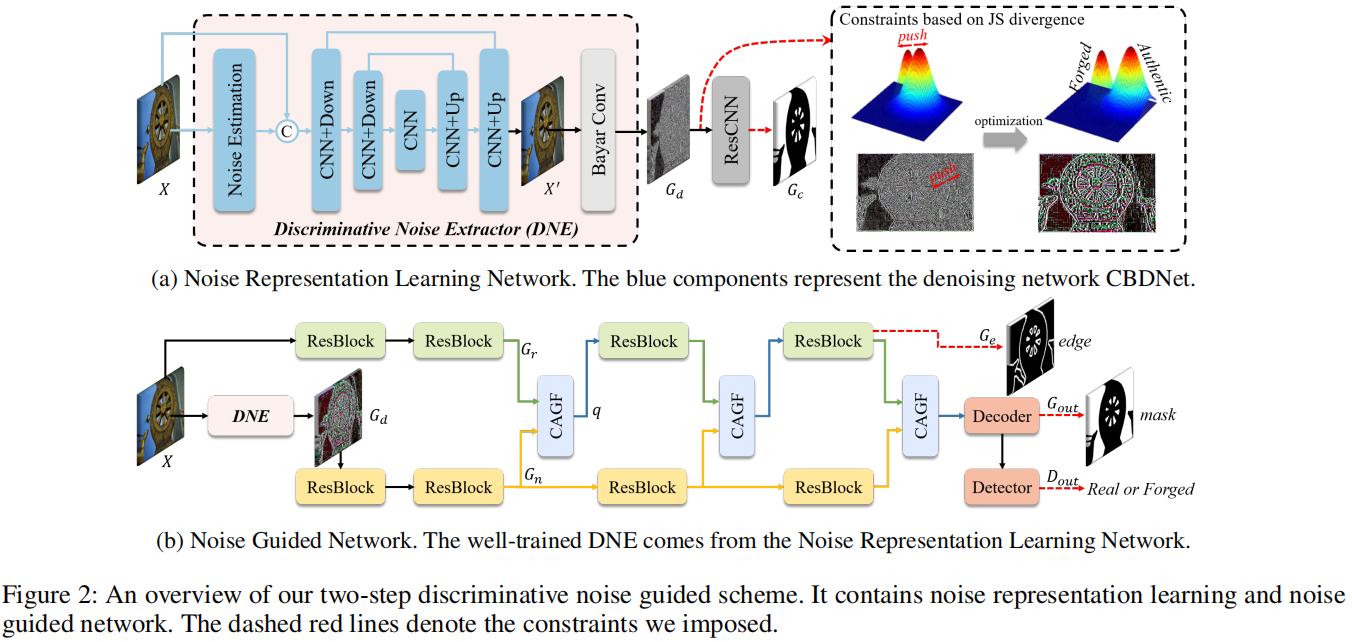
发表于AAAI2024,一种两阶段判别噪声引导的方法,第一阶段训练一个噪声提取器,以明确地扩大真实区域和伪造区域之间的噪声分布差异,第二阶段将噪声不一致和RGB数据集成,以进行伪造检测和定位。
现有问题:- 随着篡改和后处理技术的发展,这两个区域在噪声域之间的差异变得不那么明显,甚至不那么隐藏。鉴于这些缺陷,我们建议明确地学习和利用噪声的不一致性可以进一步提高IFDL的性能。
解决方案:
通过关注噪声域内的操纵痕迹来检测和定位图像伪造,一种两阶段判别噪声引导的方法,第一阶段训练一个噪声提取器,以明确地扩大真实区域和伪造区域之间的噪声分布差异,第二阶段将噪声不一致和RGB数据集成,以进行伪造检测和定位。
具体情况
一阶段: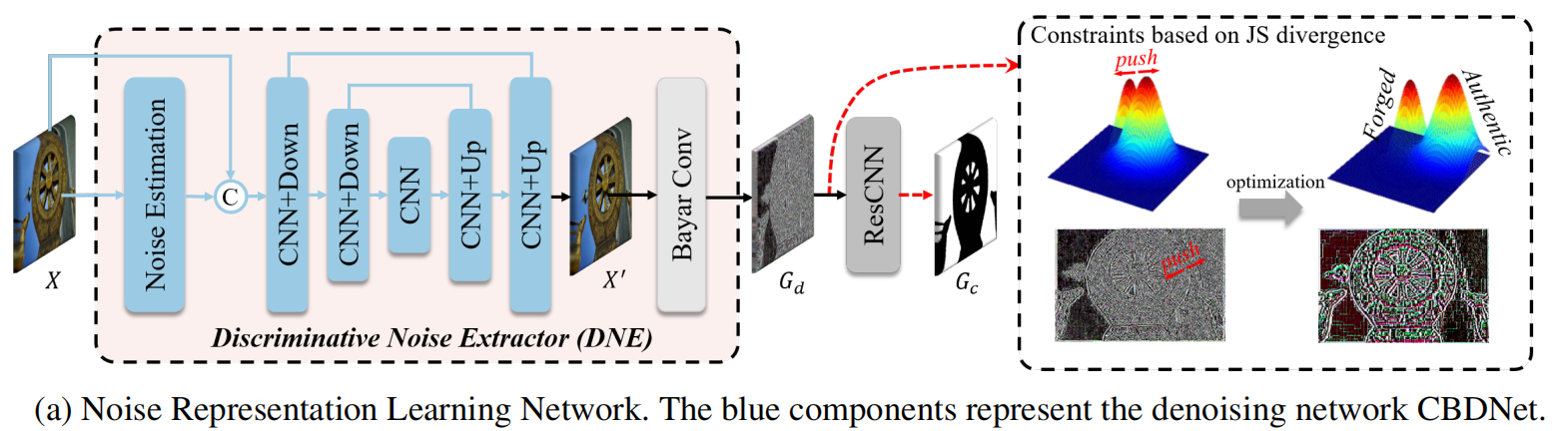 为了明确地分离出这两个区域(真实的和伪造的)的噪声分布,我们引入了JS散度来约束 $ G_d $ 。首先,我们利用 groundtruth掩模,将 $ G_d $ 划分为真实区域 $ N_a $ 的噪声和伪造区域 $ N_f $ 的噪声。
为了明确地分离出这两个区域(真实的和伪造的)的噪声分布,我们引入了JS散度来约束 $ G_d $ 。首先,我们利用 groundtruth掩模,将 $ G_d $ 划分为真实区域 $ N_a $ 的噪声和伪造区域 $ N_f $ 的噪声。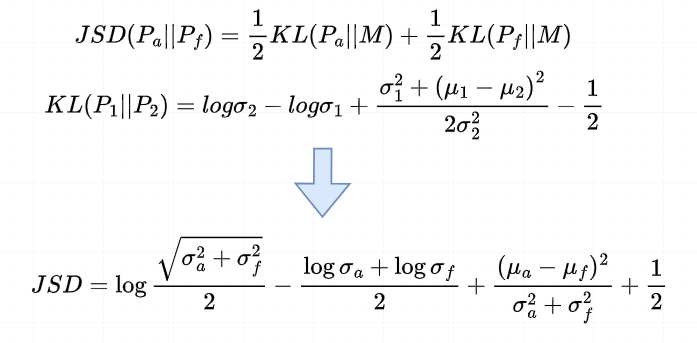 式中, $ \sigma_a $ 、 $ \sigma_f $ 为 $ N_a $ 和 $ N_f $ 的标准差, $ \mu_a $ 、 $ \mu_f $ 为 $ N_a $ 和 $ N_f $ 的平均值。
式中, $ \sigma_a $ 、 $ \sigma_f $ 为 $ N_a $ 和 $ N_f $ 的标准差, $ \mu_a $ 、 $ \mu_f $ 为 $ N_a $ 和 $ N_f $ 的平均值。$$ \mathbf{L_{n}}=\lambda\left(1-JSD\right)+\left(1-\lambda\right)\mathcal{L}\left(Y,G_{c}\right) $$ 二阶段:
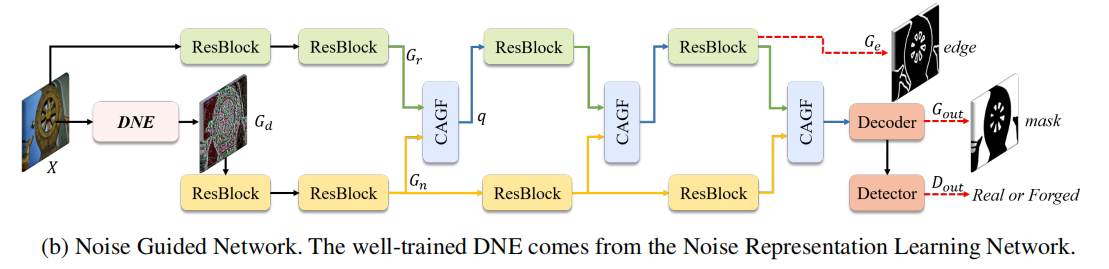 利用两个分支来处理RGB和噪声信息,为了保证噪声不一致对RGB的引导作用,我们设计了CAGF,并将其与ResNet块交替放置。在噪声的引导下,RGB分支可以提取出与篡改伪影高度相关的特征。
利用两个分支来处理RGB和噪声信息,为了保证噪声不一致对RGB的引导作用,我们设计了CAGF,并将其与ResNet块交替放置。在噪声的引导下,RGB分支可以提取出与篡改伪影高度相关的特征。
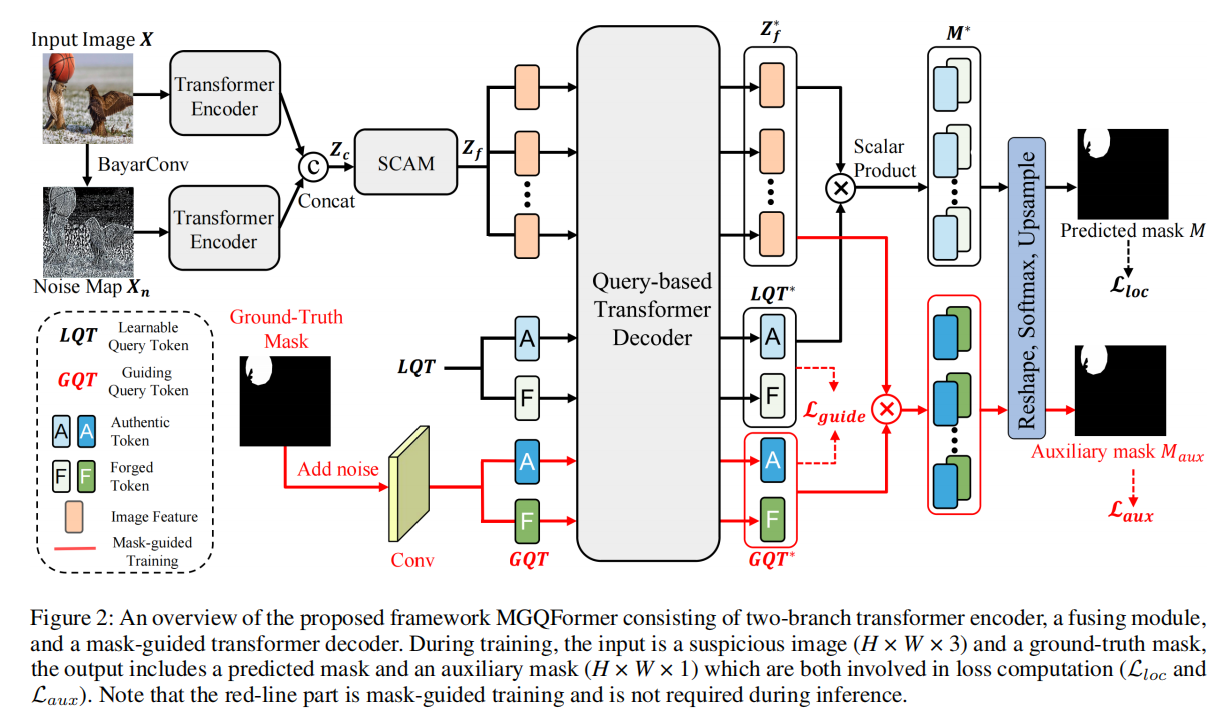
发表于AAAI2024,为应对交叉熵损失优先考虑逐像素精度,但忽略了篡改区域的空间位置和形状细节,设计了基于掩码引导查询的转换器框架(MGQFormer),该框架使用GroundTruth掩码来引导可学习查询令牌(LQT)识别伪造区域。
现有问题:- 所有现有的IMD主要通过交叉熵损失使用真值掩码,该损失优先考虑逐像素精度,但忽略了篡改区域的空间位置和形状细节。
解决方案:一种基于掩码引导查询的转换器框架(MGQFormer),该框架使用基本事实掩码来引导可学习查询令牌(LQT)识别伪造区域。
具体情况
利用BayarConv和Transformer编码器从输入图像中提取RGB和噪声特征,过空间和通道注意模块(SCAM,spatial and channel attention module)对多模态特征进行融合。其特征提取器如下: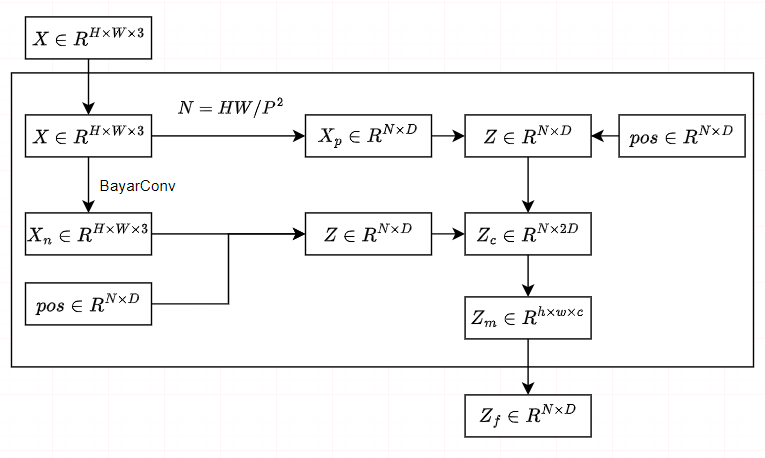 我们设计了两个可学习的查询token来表示真实和伪造的特征,它们用于在我们提出的基于查询的Transformer解码器中搜索篡改区域。为了使查询token有效参考和基于查询的解码器快速收敛,我们提出了一种利用GroundTruth掩模的空间位置和形状细节的掩模引导训练策略。其解码器如下:
我们设计了两个可学习的查询token来表示真实和伪造的特征,它们用于在我们提出的基于查询的Transformer解码器中搜索篡改区域。为了使查询token有效参考和基于查询的解码器快速收敛,我们提出了一种利用GroundTruth掩模的空间位置和形状细节的掩模引导训练策略。其解码器如下:
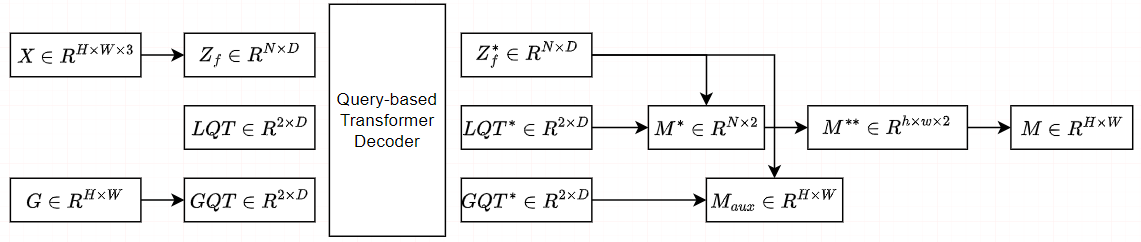 具体来说,我们将噪声的GT掩模输入MGQFrorer,以获得引导查询token(GQT)和辅助掩模 $ M_{aux} $ 。然后,利用辅助损失 $ L_{aux} $ ,使GQT包含伪造区域的空间和形状信息。此外,我们提出了一种掩模引导的损失 $ L_{guide} $ 来减小LQT和GQT之间的距离。
具体来说,我们将噪声的GT掩模输入MGQFrorer,以获得引导查询token(GQT)和辅助掩模 $ M_{aux} $ 。然后,利用辅助损失 $ L_{aux} $ ,使GQT包含伪造区域的空间和形状信息。此外,我们提出了一种掩模引导的损失 $ L_{guide} $ 来减小LQT和GQT之间的距离。
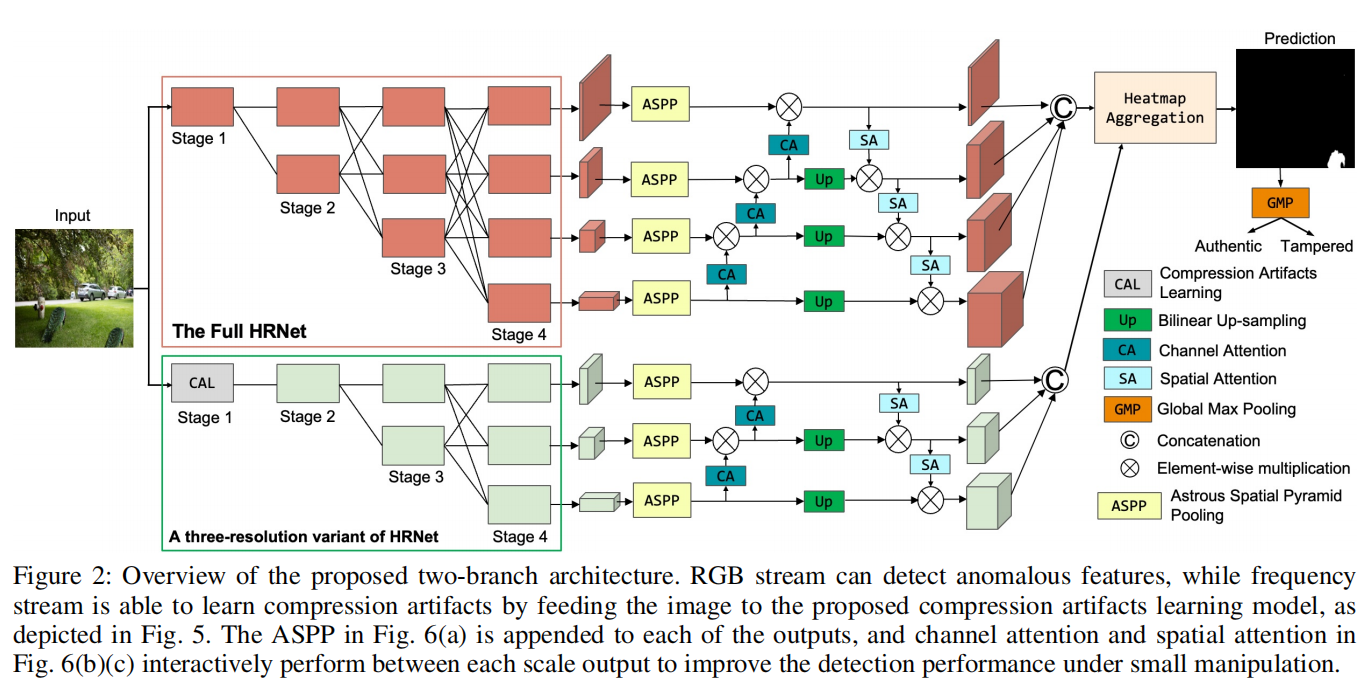
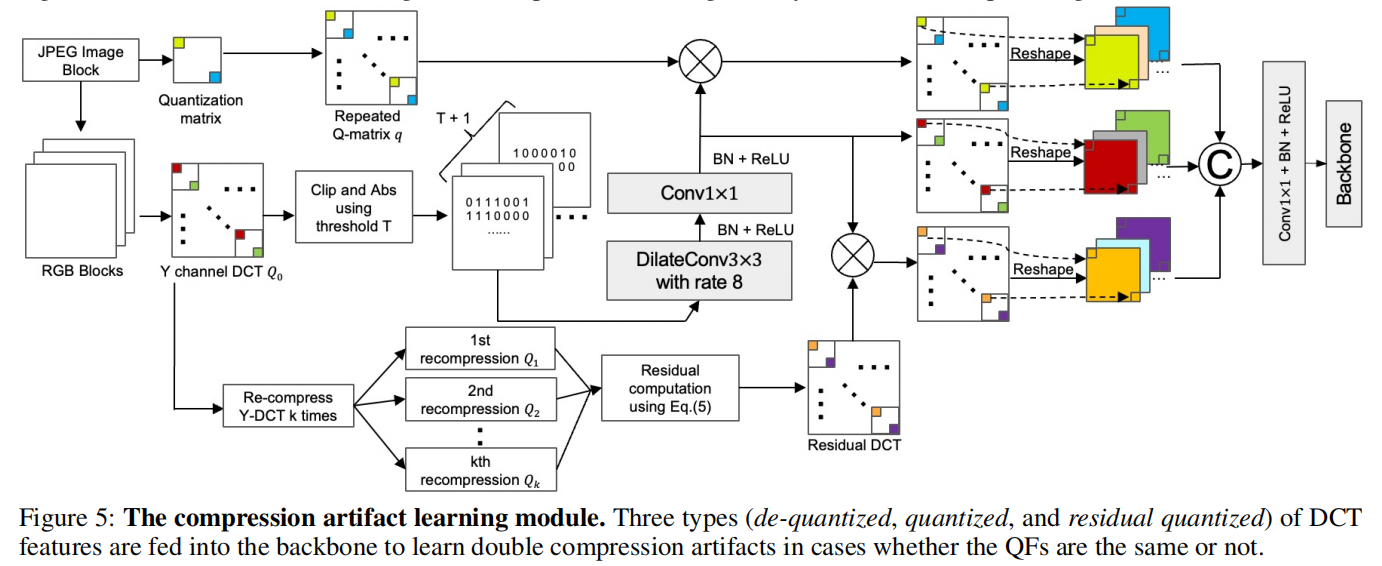
发表于AAAI2024,包含RGB和频率特征的hrnet双分支架构,能够检测双压缩伪影的压缩伪影学习模型。
现有问题:- 所有现有的IMD技术在从大图像中检测小的篡改区域时都遇到了挑战。
- 基于压缩的IMD方法在相同质量因子的双重压缩的情况下面临困难。
解决方案:包含RGB和频率特征的双分支架构,能够检测双压缩伪影的压缩伪影学习模型。
具体情况
> RGB和频率特征的双分支架构 > 双压缩伪影的压缩伪影学习模型
> 双压缩伪影的压缩伪影学习模型


发表于TMM2022,将机器学习应用到操作链检测的任务中,将每一个操作视为一个元素进行翻译。
2025年6月6日
发表于NeuralNetworks 2024。
2025年1月12日
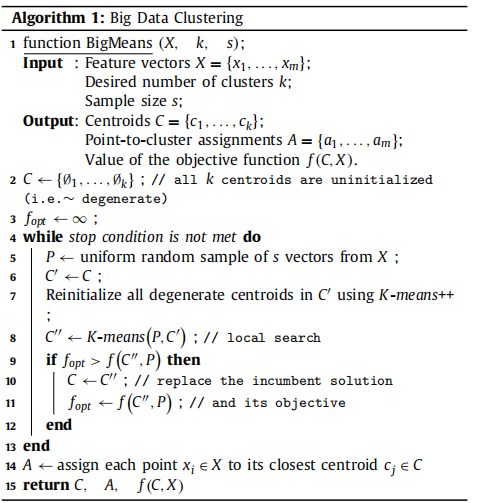
发表于Pattern Recognition 2023, 设计了一个优化kmeans的算法BigMeans。
2025年1月8日

发表于Information Fusion 2023。
2024年12月29日
发表于TCSVT 2024。
2024年12月26日
发表于IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2023,提出了DAFC来自动分组图像,得到的迭代优化问题可以通过小批量RMSprop和反向传播而不是SGD有效地解决,可以学习一个更聚类友好的瓶颈空间。
2024年12月23日
发表于Pattern Recognition 2023,基于深度学习的图像伪造检测综述。
2024年12月18日
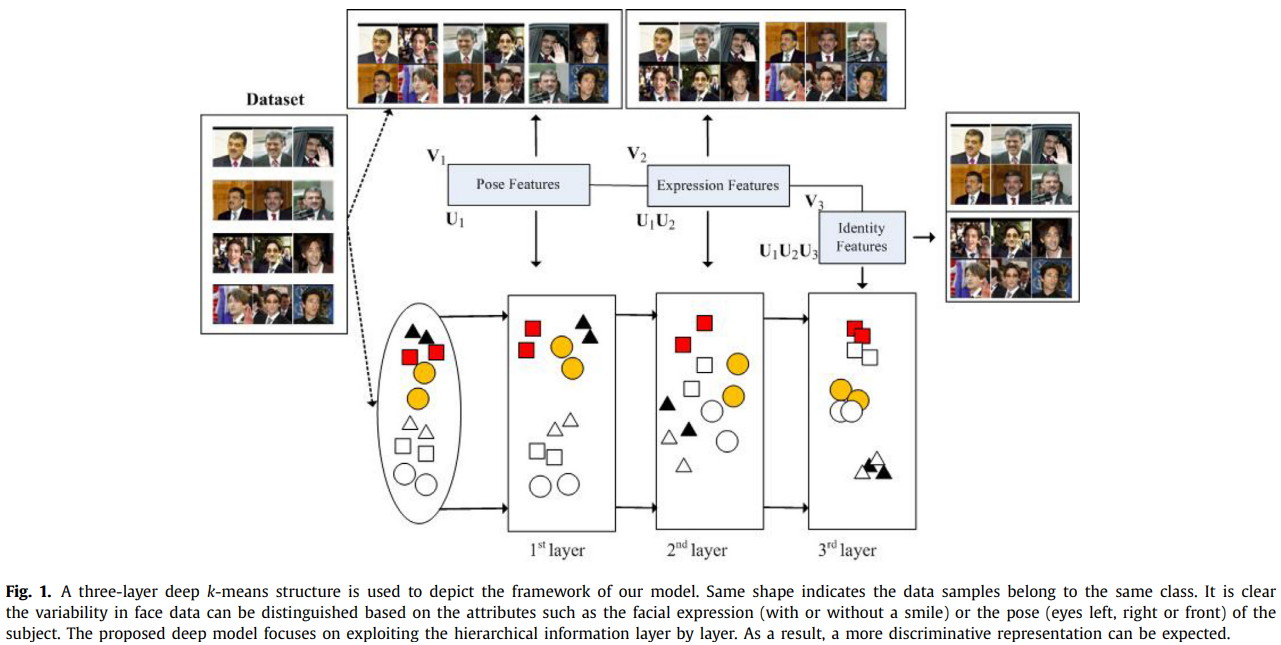
发表于IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems 2019,提出了深度模糊k-means(DFKM),具有加权自适应损失函数的FKM。
2024年12月4日
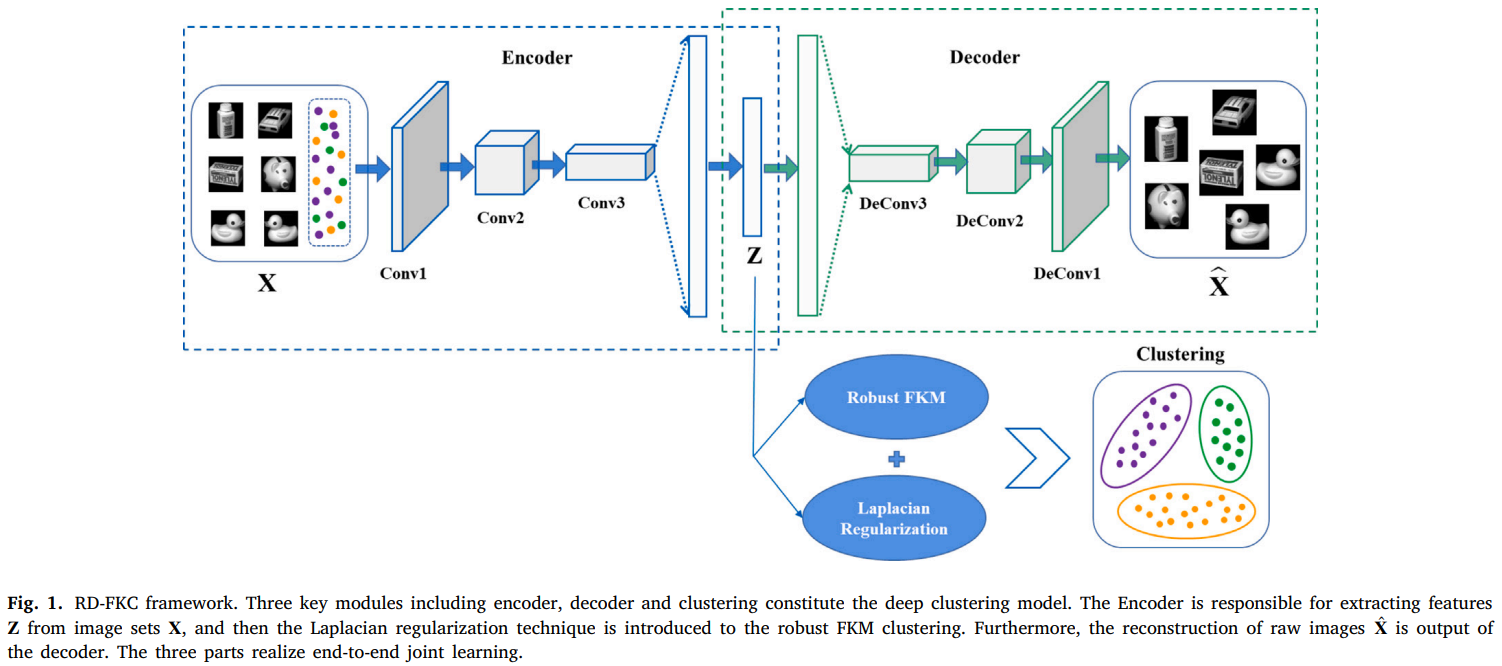
发表于JCR一区、CCF B类期刊的Pattern Recognition 2024,提出了一种新的边界引导图像篡改定位模型,该模型通过精心设计的注意力和对比学习机制充分利用被篡改区域的边界信息,利用拉普拉斯正则化方法对隶属度矩阵进行约束,使从相似样本中学习到的隶属度也相互关联,将自适应损失函数引入到统一的框架中,可以减少各种异常值的影响,有助于增强聚类的鲁棒性。
2024年12月3日
发表于Information Sciences 2023。
2024年12月2日
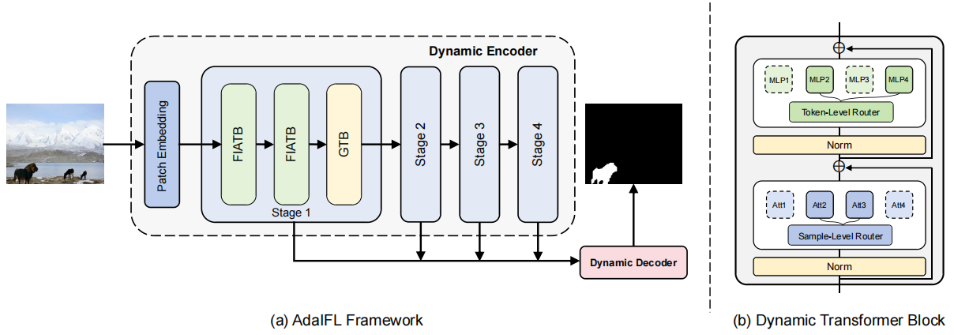
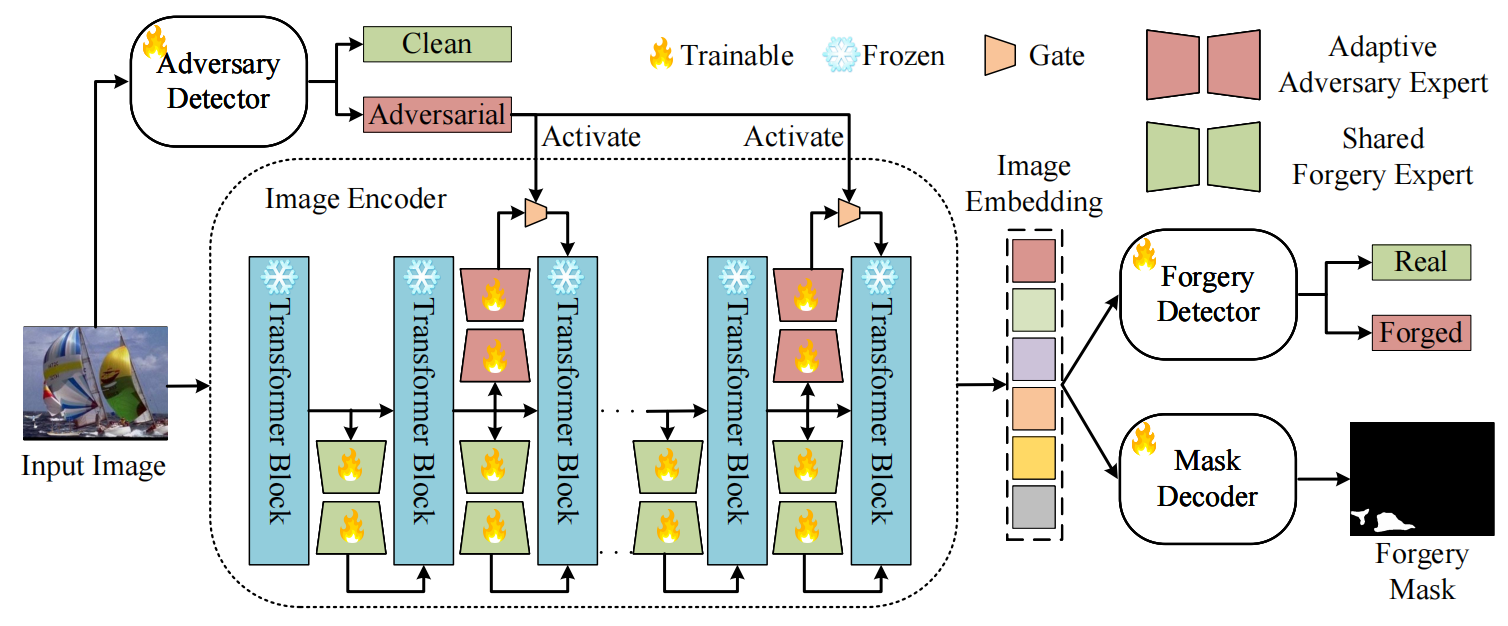
发表于ECCV2024,提出了AdaIFL,为不同的网络组件定制不同的专家组,构建多个不同的特征子空间,利用自适应激活的专家网络,AdaIFL可以捕获与伪造模式相关的判别特征,增强了模型的泛化能力。提出了一种特征重要性感知注意力,自适应地感知不同区域的重要性,并将区域特征聚集成可变长度的标记,将模型的注意力导向更有区别和信息的区域。
2024年11月19日
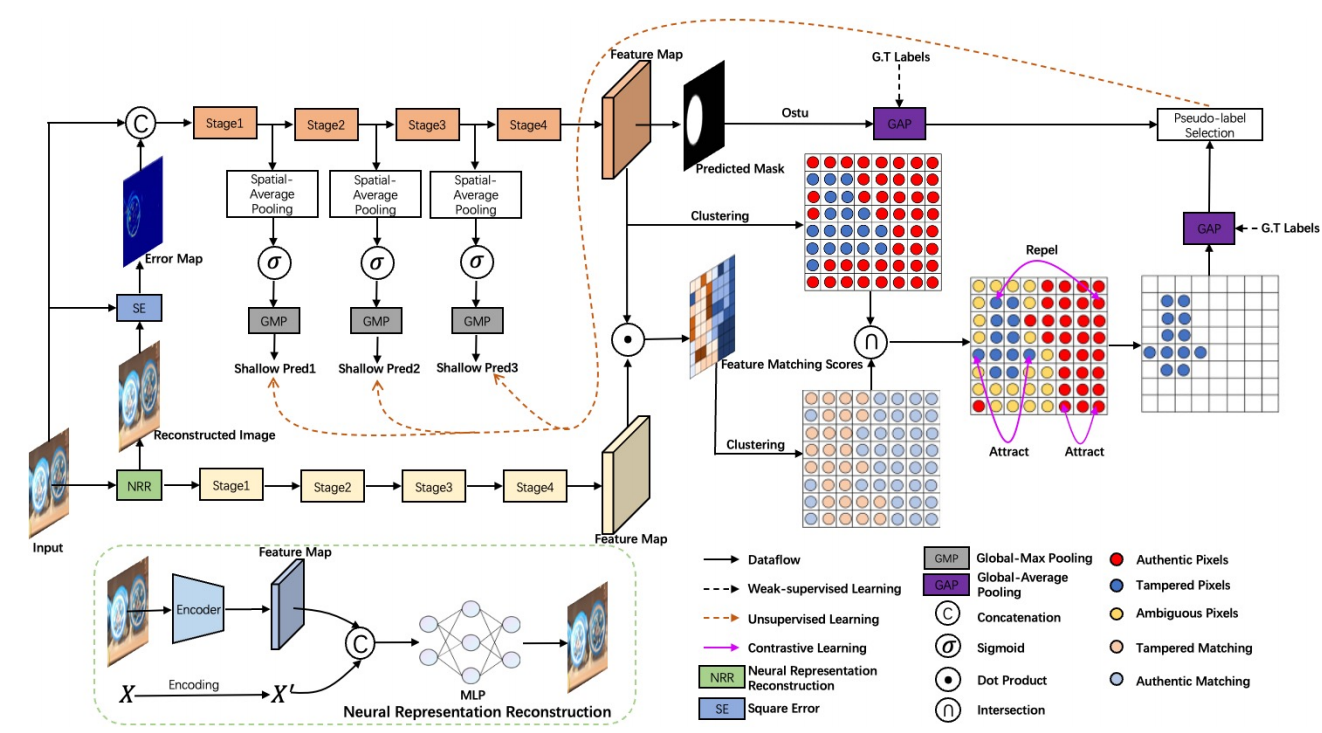
发表于ECCV 2024。
2024年11月19日
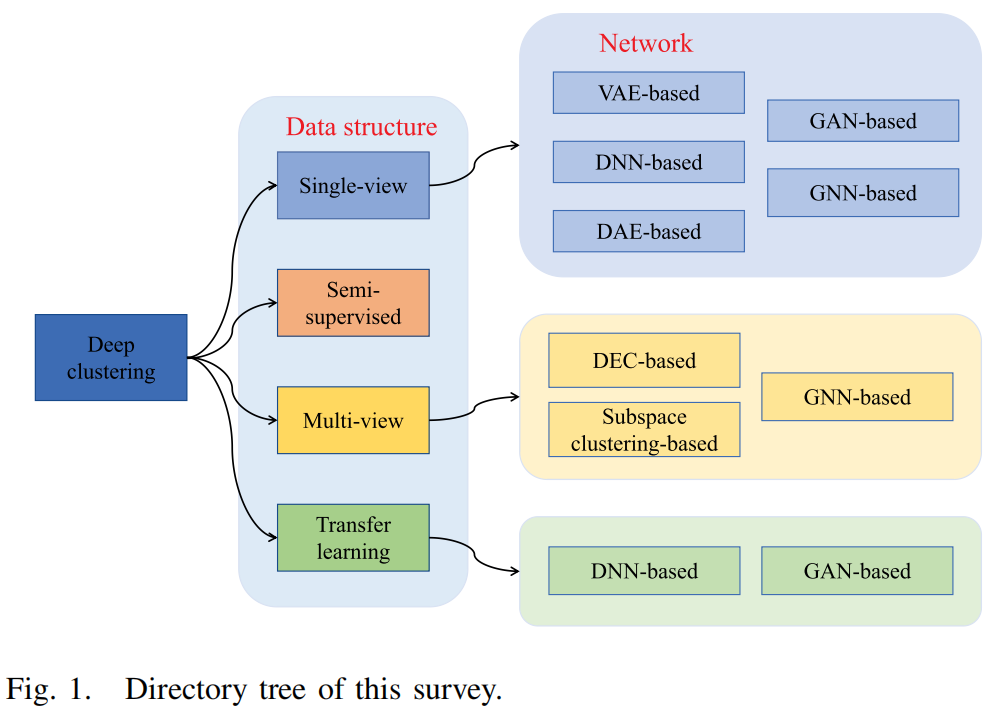
发表于IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2024,深度聚类的综合综述。
2024年9月29日

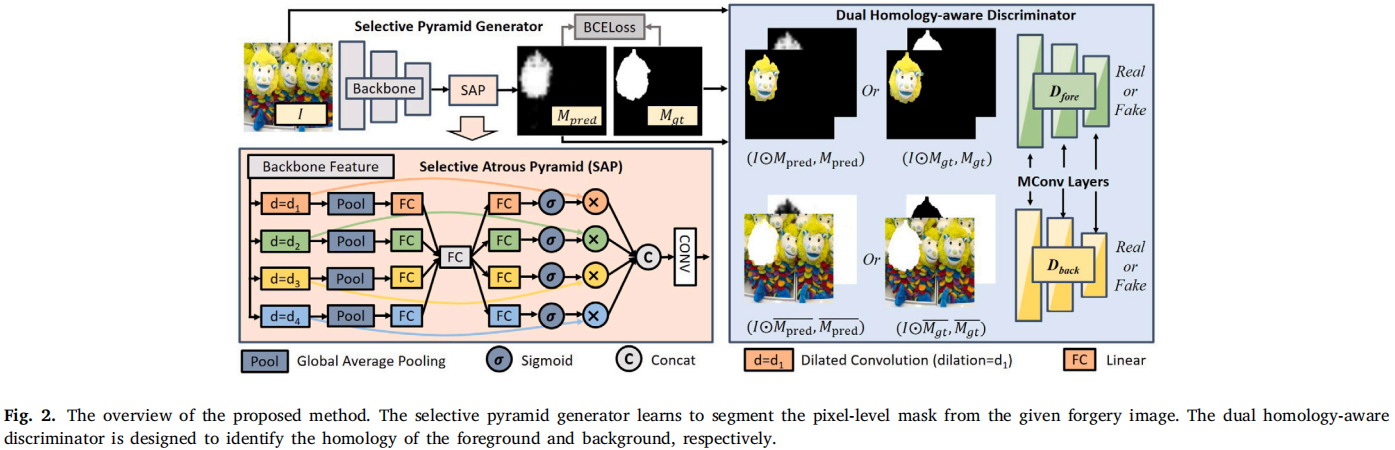
发表于Pattern Recognition 2024,双同源感知生成对抗网络(DH-GAN),选择性金字塔(SAP)校准多尺度特征。
2024年8月24日
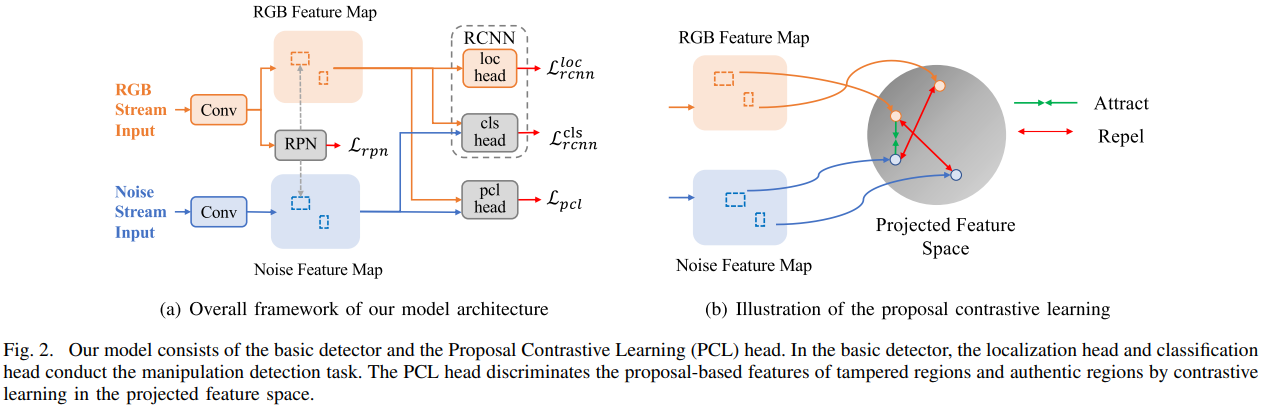
发表于TCSVT 2023。
2024年5月5日
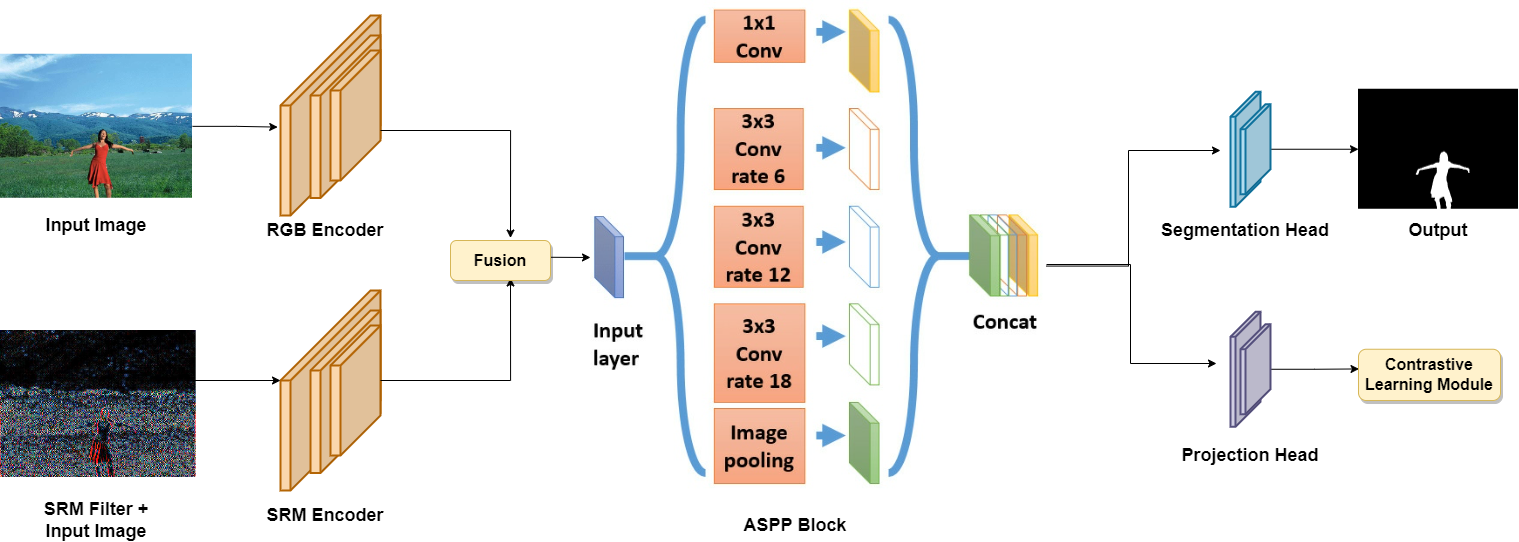
发表于WACV 2023,RGB频域双通道多尺度特征网络。
2024年4月10日
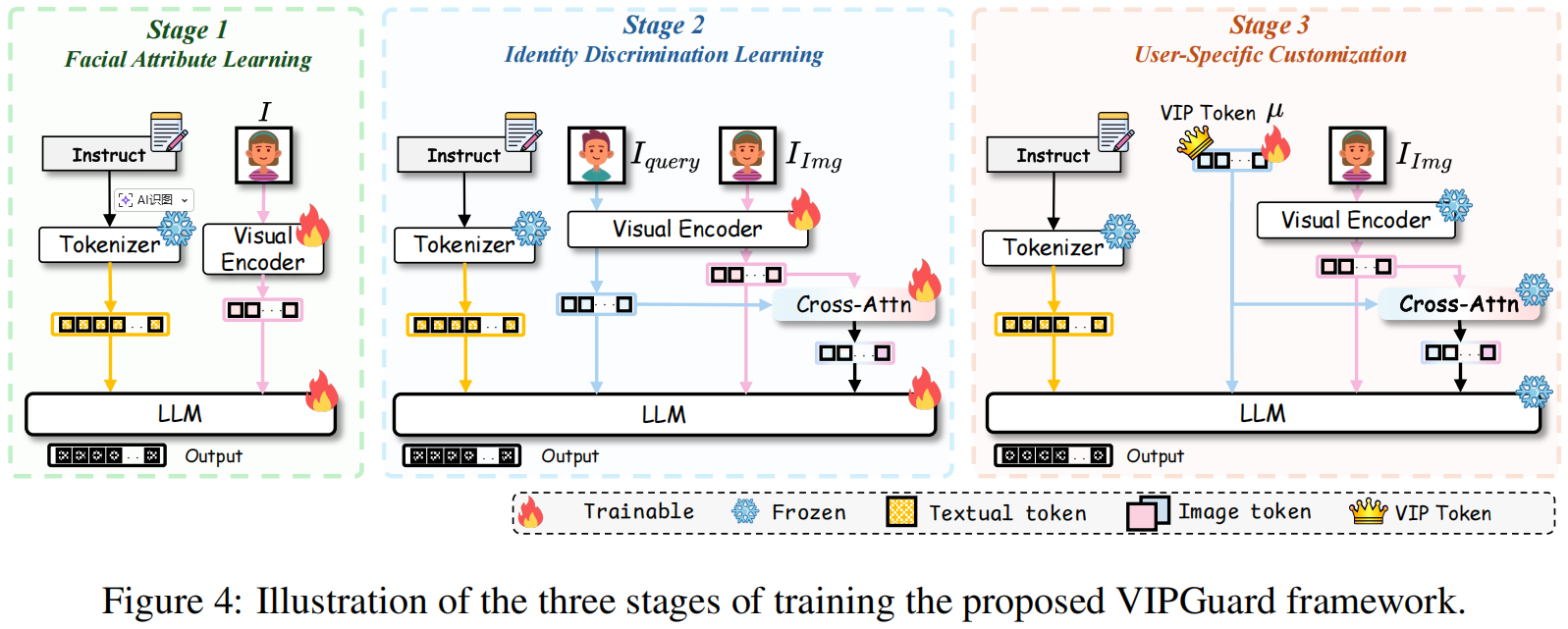
aixiv文章,基于大语言模型完成人脸篡改的检测任务,其核心的创新点是利用已知面部特征实现个性化、精准且可解释的检测框架VIPGuard。评价:其提出来一种新的MLLM的训练模式,第一阶段让MLLM正确描述人脸,第二阶段让MLLM正确区分人脸,第三阶段让MLLM正确认识给定的身份信息。 - 人脸篡改检测 - MLLM
2025年12月15日
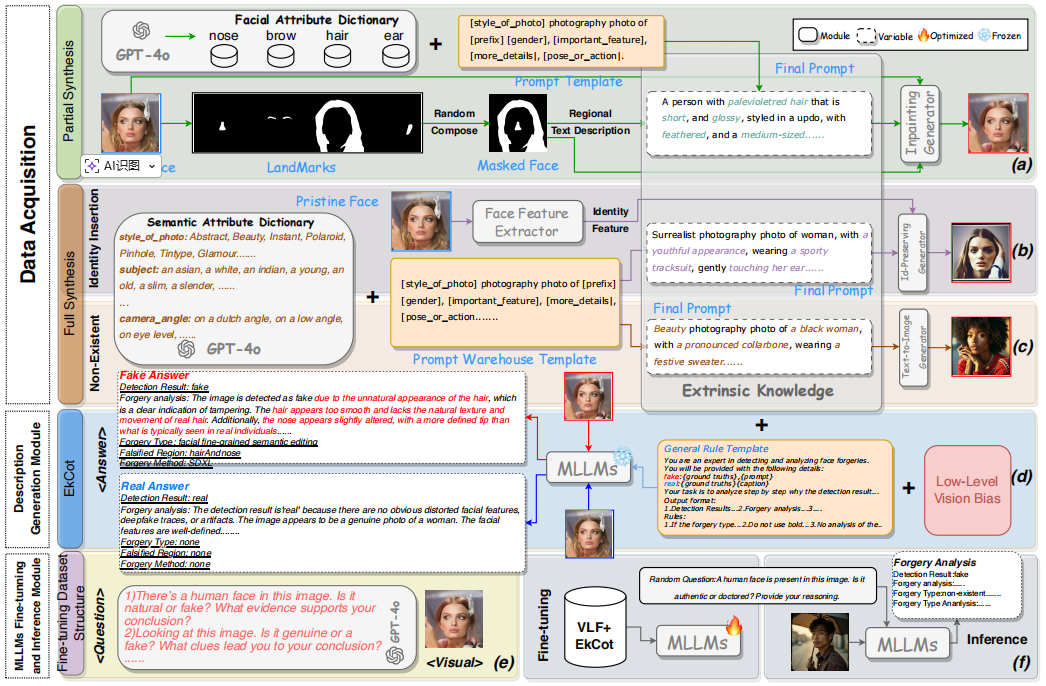
aixiv文章,基于大语言模型完成人脸篡改的检测、定位和溯源任务,其核心的创新点是构建了部分合成面部数据集,以及一个基于MLLM的LoRA微调模型和一个基于MLLM的篡改思维链EKCot。评价:其使用低级视觉模型对图片的多个方面打分作为视觉低级线索,然后和精心设计的prompt拼接来微调大语言模型MLLM。 - 人脸篡改检测 - MLLM
2025年12月9日
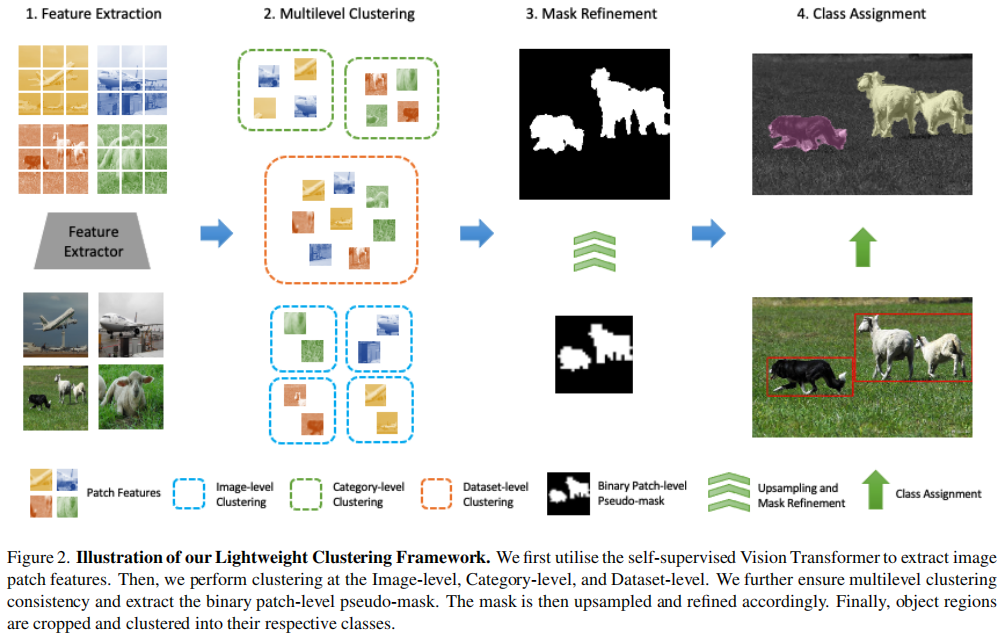
aixiv文章,面对无监督语义分割,使用多级聚类的方法来实现。
2025年2月15日
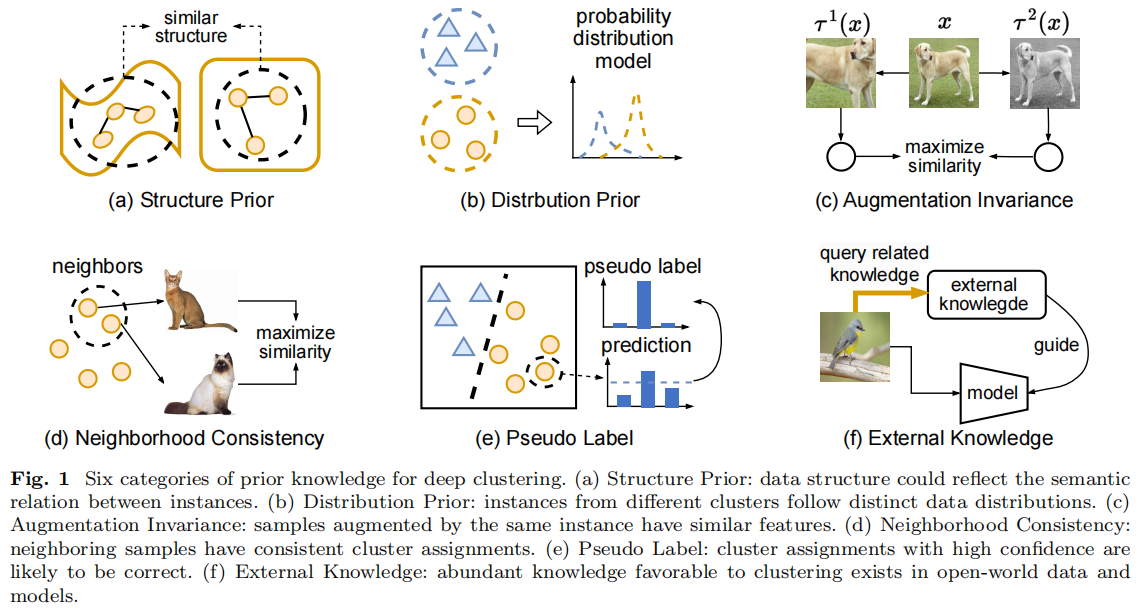
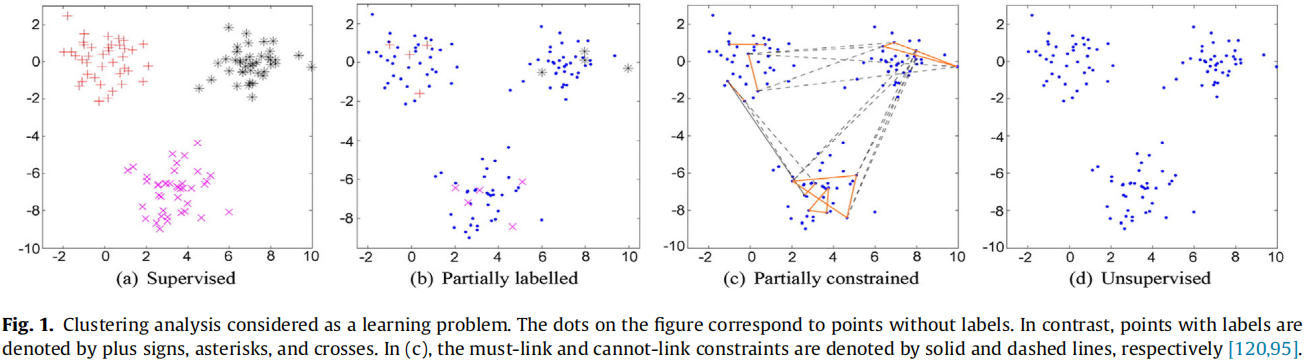
发表于Vicinagearth 2024,从先验的角度看深度聚类方法,(a)结构先验:数据结构可以反映实例之间的语义关系。(b)分布先验:来自不同集群的实例遵循不同的数据分布。(c)增强不变性:由相同实例增强的样本具有相似的特征。(d)邻域一致性:相邻的样本具有一致的聚类分配。(e)伪标签:具有高可信度的聚类分配很可能是正确的。(f)外部知识:在开放世界的数据和模型中存在大量有利于聚类的知识。
2025年1月7日